Spontaneous activity in the developing gerbil auditory cortex in vivo involves GABAergic transmission
- PMID: 22986170
- PMCID: PMC4106364
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.09.008
Spontaneous activity in the developing gerbil auditory cortex in vivo involves GABAergic transmission
Abstract
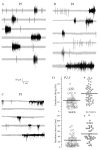
A salient feature of the developing brain is that spontaneous oscillations (SOs) and waves may influence the emergence of synaptic connections. While GABA produces depolarization and may support SOs in the neurons of developing rodents, it elicits hyperpolarization and diminishes SOs in developing gerbil auditory cortex (ACx). Therefore, we asked whether SOs exist in developing gerbil ACx in vivo and if GABAergic involvement can be manipulated. In vivo extracellular recordings in P3-5 ACx revealed SOs with longer burst durations and shorter inter-event intervals compared to ACx SOs in slices. ACx was then validated by gross anatomical features and lesions created at the in vivo recording site that corresponded with the electrophysiological coordinates of thalamorecipient ACx in slices. Further, NeuroVue Red, a lipophilic dye loaded at the in vivo recording sites, stained anatomically identifiable fiber tracks between the ACx and the auditory thalamus, medial geniculate body (MG). Separately, to chronically perturb GABAergic role in SOs, P2-5 pups were administered daily with GABA(A) receptor blocker, bicuculline (BIC). We then recorded from P14-17 ACx neurons in slices generated after hearing onset. ACx neurons from BIC-administered pups exhibited spontaneous action potentials in contrast to subthreshold synaptic potentials in neurons from sham-injected animals. Finally, to elucidate whether the gap junction blocker mefloquine (MFQ) previously shown to dampen ACx SOs in slices affected GABAergic transmission, MFQ was acutely applied in P3-5 slices while spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents (sIPSCs) were recorded. Whereas MFQ increased the amplitude and frequency of sIPSCs in ACx neurons, the broad-spectrum gap junction blocker carbenoxolone decreased sIPSC amplitudes only. Together, we show that P2-5 gerbil ACx can endogenously generate SOs in vivo. Persistence of activity in ACx in P14-17 slices from pups administered with BIC at P2-5 implies that inhibitory GABAergic activity linked with gap-junction participates in the maturation of ACx.
Copyright © 2012 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Developmental expression of endogenous oscillations and waves in the auditory cortex involves calcium, gap junctions, and GABA.Neuroscience. 2007 Jun 8;146(4):1629-39. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.03.039. Epub 2007 May 3. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17478052
-
Hearing loss prevents the maturation of GABAergic transmission in the auditory cortex.Cereb Cortex. 2008 Sep;18(9):2098-108. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhm233. Epub 2008 Jan 24. Cereb Cortex. 2008. PMID: 18222937 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of auditory synaptic inputs to gerbil perirhinal cortex.Front Neural Circuits. 2015 Aug 14;9:40. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2015.00040. eCollection 2015. Front Neural Circuits. 2015. PMID: 26321918 Free PMC article.
-
Propagation of postsynaptic currents and potentials via gap junctions in GABAergic networks of the rat hippocampus.J Physiol. 2007 Jan 15;578(Pt 2):527-44. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.123463. Epub 2006 Nov 16. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17110410 Free PMC article.
-
Plasticity in auditory cortex during parenthood.Hear Res. 2023 Apr;431:108738. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2023.108738. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Hear Res. 2023. PMID: 36931020 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroauditory toxicity of artemisinin combination therapies-have safety concerns been addressed?Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2014 Jul;91(1):62-73. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.13-0702. Epub 2014 May 27. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2014. PMID: 24865683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging functional connectivity differences in newborn infants vulnerable to autism spectrum disorders.Transl Psychiatry. 2020 May 6;10(1):131. doi: 10.1038/s41398-020-0805-y. Transl Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32376820 Free PMC article.
-
Specific synaptopathies diversify brain responses and hearing disorders: you lose the gain from early life.Cell Tissue Res. 2015 Jul;361(1):77-93. doi: 10.1007/s00441-015-2168-x. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Cell Tissue Res. 2015. PMID: 25843689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasticity of neonatal neuronal networks in very premature infants: Source localization of temporal theta activity, the first endogenous neural biomarker, in temporoparietal areas.Hum Brain Mapp. 2017 May;38(5):2345-2358. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23521. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Hum Brain Mapp. 2017. PMID: 28112458 Free PMC article.
-
Differential signaling to subplate neurons by spatially specific silent synapses in developing auditory cortex.J Neurosci. 2014 Jun 25;34(26):8855-64. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0233-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24966385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adelsberger H, Garaschuk O, Konnerth A. Cortical calcium waves in resting newborn mice. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:988–990. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y. Excitatory actions of GABA during development: the nature of the nurture. Nat Rev Neursoci. 2002;3:728–739. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y, Gaiarsa JL, Tyzio R, Khazipov R. GABA: a pioneer transmitter that excites immature neurons and generates primitive oscillations. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:1215–1284. - PubMed
-
- Büdinger Heil P., Scheich H. Functional organization of auditory cortex in the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). Anatomical subdivisions and corticocortical connections. Eur J Neurosci. 2000;12:2425–2451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

