Smoothened transduces Hedgehog signal by forming a complex with Evc/Evc2
- PMID: 22986504
- PMCID: PMC3494391
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2012.134
Smoothened transduces Hedgehog signal by forming a complex with Evc/Evc2
Abstract
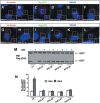
Hedgehog (Hh) signaling plays pivotal roles in embryonic development and adult tissue homeostasis in species ranging from Drosophila to mammals. The Hh signal is transduced by Smoothened (Smo), a seven-transmembrane protein related to G protein coupled receptors. Despite a conserved mechanism by which Hh activates Smo in Drosophila and mammals, how mammalian Hh signal is transduced from Smo to the Gli transcription factors is poorly understood. Here, we provide evidence that two ciliary proteins, Evc and Evc2, the products of human disease genes responsible for the Ellis-van Creveld syndrome, act downstream of Smo to transduce the Hh signal. We found that loss of Evc/Evc2 does not affect Sonic Hedgehog-induced Smo phosphorylation and ciliary localization but impedes Hh pathway activation mediated by constitutively active forms of Smo. Evc/Evc2 are dispensable for the constitutive Gli activity in Sufu(-/-) cells, suggesting that Evc/Evc2 act upstream of Sufu to promote Gli activation. Furthermore, we demonstrated that Hh stimulates binding of Evc/Evc2 to Smo depending on phosphorylation of the Smo C-terminal intracellular tail and that the binding is abolished in Kif3a(-/-) cilium-deficient cells. We propose that Hh activates Smo by inducing its phosphorylation, which recruits Evc/Evc2 to activate Gli proteins by antagonizing Sufu in the primary cilia.
Figures
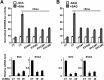
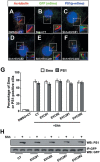
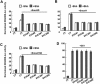
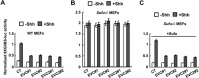

References
-
- Ingham PW, McMahon AP. Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes Dev. 2001;15:3059–3087. - PubMed
-
- Nusslein-Volhard C, Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature. 1980;287:795–801. - PubMed
-
- Jiang J. Regulation of Hh/Gli signaling by dual ubiquitin pathways. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:2457–2463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

