Quantitative microtiter fibronectin fibrillogenesis assay: use in high throughput screening for identification of inhibitor compounds
- PMID: 22986508
- PMCID: PMC3508085
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2012.07.003
Quantitative microtiter fibronectin fibrillogenesis assay: use in high throughput screening for identification of inhibitor compounds
Abstract
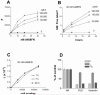
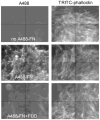
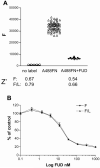
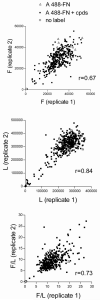
Fibronectin (FN) is a plasma glycoprotein that circulates in the near micromolar concentration range and is deposited along with locally produced FN in the extracellular matrices of many tissues. The control of FN deposition is tightly controlled by cells. Agents that modulate FN assembly may be useful therapeutically in conditions characterized by excessive FN deposition, such as fibrosis, inflammatory diseases, and malignancies. To identify such agents by high throughput screening (HTS), we developed a microtiter assay of FN deposition by human fibroblasts. The assay provides a robust read-out of FN assembly. Alexa 488-FN (A488-FN) was added to cell monolayers, and the total fluorescence intensity of deposited A488-FN was quantified. The fluorescence intensity of deposited A488-FN correlated with the presence of FN fibrils visualized by fluorescence microscopy. The assay Z' values were 0.67 or 0.54, respectively, when using background values of fluorescence either with no added A488-FN or with A488-FN added together with a known inhibitor of FN deposition. The assay was used to screen libraries comprising 4160 known bioactive compounds. Nine compounds were identified as non- or low-cytotoxic inhibitors of FN assembly. Four (ML-9, HA-100, tyrphostin and imatinib mesylate) are kinase inhibitors, a category of compounds known to inhibit FN assembly; two (piperlongumine and cantharidin) are promoters of cancer cell apoptosis; and three (maprotiline, CGS12066B, and aposcopolamine) are modulators of biogenic amine signaling. The latter six compounds have not been recognized heretofore as affecting FN assembly. The assay is straight-forward, adapts to 96- and 384-well formats, and should be useful for routine measurement of FN deposition and HTS. Screening of more diverse chemical libraries and identification of specific and efficient modulators of FN fibrillogenesis may result in therapeutics to control excessive connective tissue deposition.
Copyright © 2012 International Society of Matrix Biology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Allen-Hoffmann BL, Mosher DF. Matrix assembly sites for exogenous fibronectin are decreased on human fibroblasts after treatment with agents which increase intracellular cAMP. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:14361–14365. - PubMed
-
- Blum G, Gazit A, Levitzki A. Development of new insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor kinase inhibitors using catechol mimics. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:40442–40454. - PubMed
-
- Chen TC, Hinton DR, Zidovetzki R, Hofman FM. Up-regulation of the cAMP/PKA pathway inhibits proliferation, induces differentiation, and leads to apoptosis in malignant gliomas. Lab Invest. 1998;78:165–174. - PubMed
-
- Chernousov MA, Fogerty FJ, Koteliansky VE, Mosher DF. Role of the I-9 and III-1 modules of fibronectin in formation of an extracellular fibronectin matrix. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:10851–10858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

