Molecular characterisation of murine acute myeloid leukaemia induced by 56Fe ion and 137Cs gamma ray irradiation
- PMID: 22987027
- PMCID: PMC3716295
- DOI: 10.1093/mutage/ges055
Molecular characterisation of murine acute myeloid leukaemia induced by 56Fe ion and 137Cs gamma ray irradiation
Abstract
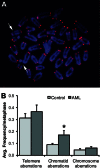
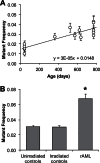
Exposure to sparsely ionising gamma- or X-ray irradiation is known to increase the risk of leukaemia in humans. However, heavy ion radiotherapy and extended space exploration will expose humans to densely ionising high linear energy transfer (LET) radiation for which there is currently no understanding of leukaemia risk. Murine models have implicated chromosomal deletion that includes the hematopoietic transcription factor gene, PU.1 (Sfpi1), and point mutation of the second PU.1 allele as the primary cause of low-LET radiation-induced murine acute myeloid leukaemia (rAML). Using array comparative genomic hybridisation, fluorescence in situ hybridisation and high resolution melt analysis, we have confirmed that biallelic PU.1 mutations are common in low-LET rAML, occurring in 88% of samples. Biallelic PU.1 mutations were also detected in the majority of high-LET rAML samples. Microsatellite instability was identified in 42% of all rAML samples, and 89% of samples carried increased microsatellite mutant frequencies at the single-cell level, indicative of ongoing instability. Instability was also observed cytogenetically as a 2-fold increase in chromatid-type aberrations. These data highlight the similarities in molecular characteristics of high-LET and low-LET rAML and confirm the presence of ongoing chromosomal and microsatellite instability in murine rAML.
Figures


References
-
- Shimizu Y., Kato H., Schull W. J. (1991). Risk of cancer among atomic bomb survivors. J. Radiat. Res 32 Suppl 2, 54–63 - PubMed
-
- Cardis E., Gilbert E. S., Carpenter L., et al. (1995). Effects of low doses and low dose rates of external ionizing radiation: cancer mortality among nuclear industry workers in three countries. Radiat. Res 142, 117–132 - PubMed
-
- Wright J. D., St Clair C. M., Deutsch I., Burke W. M., Gorrochurn P., Sun X., Herzog T. J. (2010). Pelvic radiotherapy and the risk of secondary leukemia and multiple myeloma. Cancer 116, 2486–2492 - PubMed
-
- Travis L. B., Andersson M., Gospodarowicz M., et al. (2000). Treatment-associated leukemia following testicular cancer. J. Natl Cancer Inst 92, 1165–1171 - PubMed
-
- Smith S. M., Le Beau M. M., Huo D., Karrison T., Sobecks R. M., Anastasi J., Vardiman J. W., Rowley J. D., Larson R. A. (2003). Clinical-cytogenetic associations in 306 patients with therapy-related myelodysplasia and myeloid leukemia: the University of Chicago series. Blood 102, 43–52 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

