Amyloid-β induced signaling by cellular prion protein and Fyn kinase in Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 22987042
- PMCID: PMC3609048
- DOI: 10.4161/pri.22212
Amyloid-β induced signaling by cellular prion protein and Fyn kinase in Alzheimer disease
Abstract
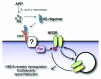
Alzheimer disease (AD) is the most prevalent cause of dementia. Amyloid-β (Aβ) oligomers are potent synaptotoxins thought to mediate AD-related phenotypes. Cellular prion protein (PrP(C)) has been identified as a high-affinity receptor for Aβ oligomers. Herein, we review the functional consequences of Aβ oligomer binding to PrP(C) on the neuronal surface. We highlight recent evidence that Fyn kinase mediates signal transduction downstream of the PrP(C)-Aβ oligomer complex. These studies suggest that PrP(C) has a central role in AD pathogenesis and may provide a target for therapeutic intervention in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; Fyn kinase; PrpC; cellular prion protein; prion.
Figures
References
-
- Wimo A, Prince M. World Alzheimer Report 2010: The Global Economic Impact of Dementia (London: Alzheimer's Disease International). 2010: p. 1-56.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
