Donor polymorphisms of toll-like receptor 4 associated with graft failure in liver transplant recipients
- PMID: 22987288
- PMCID: PMC3518641
- DOI: 10.1002/lt.23549
Donor polymorphisms of toll-like receptor 4 associated with graft failure in liver transplant recipients
Abstract
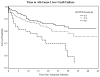
There have been many reports showing significant associations between recipient genetic variants and allograft outcomes, including acute rejection and graft failure, but less is known about the contribution of the donor genotype. We analyzed 37 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) gene from deceased donor liver allografts transplanted into 738 recipients to determine their effects on liver graft failure (LGF). Two SNPs exhibited a significant association with LGF after adjustments for donor race and recipient race and corrections for multiple test comparisons: rs11536865 [hazard ratio (HR) = 2.5, P = 0.0003] and rs5030717 (HR = 1.67, P = 0.0008). An additional SNP, rs913930, exhibited a significant association in Caucasian donors (HR = 1.62, P = 0.0006), and 2 SNPs exhibited a suggestive association in African American donors: rs11536865 (HR = 2.45, P = 0.002) and rs5030717 (HR = 2.32, P = 0.002). Additionally, the liver donor risk index (HR = 2.56, 95% confidence interval = 1.54-4.26, P = 0.0003) and the recipient hepatitis C virus (HCV) status (HR = 1.53, 95% confidence interval = 1.04-2.24, P = 0.032) increased the risk of all-cause LGF in a Cox proportional hazards model adjusted for recipient race. Donor polymorphisms in TLR4 could be important factors in modulating TLR4 activity and, therefore, affect the risk of graft loss. Additionally, there is a suggestion of an interaction between polymorphisms within TLR4 and the HCV status.
Copyright © 2012 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Hauser IA, Kruck S, Gauer S, Nies AT, Winter S, Bedke J, et al. Human pregnane x receptor genotype of the donor but not of the recipient is a risk factor for delayed graft function after renal transplantation. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012;91:905–916. - PubMed
-
- Cervera C, Balderramo D, Suárez B, Prieto J, Fuster F, Linares L, et al. Donor mannose-binding lectin gene polymorphisms influence the outcome of liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2009;15:1217–1224. - PubMed
-
- Buis CI, van der Steege G, Visser DS, Nolte IM, Hepkema BG, Nijsten M, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 genotype of the donor is associated with graft survival after liver transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2008;8:377–385. - PubMed
-
- Hwang YH, Ro H, Choi I, Kim H, Oh KH, Hwang JI, et al. Impact of polymorphisms of TLR4/CD14 and TLR3 on acute rejection in kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 2009;88:699–705. - PubMed
-
- Mutlubas F, Mir S, Berdeli A, Ozkayin N, Sozeri B. Association between Toll-like receptors 4 and 2 gene polymorphisms with chronic allograft nephropathy in Turkish children. Transplant Proc. 2009;41:1589–1593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical