Nonlocal regularization for active appearance model: Application to medial temporal lobe segmentation
- PMID: 22987811
- PMCID: PMC6869426
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.22183
Nonlocal regularization for active appearance model: Application to medial temporal lobe segmentation
Abstract
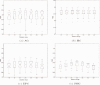
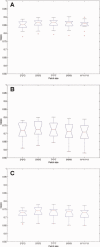
The human medial temporal lobe (MTL) is an important part of the limbic system, and its substructures play key roles in learning, memory, and neurodegeneration. The MTL includes the hippocampus (HC), amygdala (AG), parahippocampal cortex (PHC), entorhinal cortex, and perirhinal cortex--structures that are complex in shape and have low between-structure intensity contrast, making them difficult to segment manually in magnetic resonance images. This article presents a new segmentation method that combines active appearance modeling and patch-based local refinement to automatically segment specific substructures of the MTL including HC, AG, PHC, and entorhinal/perirhinal cortex from MRI data. Appearance modeling, relying on eigen-decomposition to analyze statistical variations in image intensity and shape information in study population, is used to capture global shape characteristics of each structure of interest with a generative model. Patch-based local refinement, using nonlocal means to compare the image local intensity properties, is applied to locally refine the segmentation results along the structure borders to improve structure delimitation. In this manner, nonlocal regularization and global shape constraints could allow more accurate segmentations of structures. Validation experiments against manually defined labels demonstrate that this new segmentation method is computationally efficient, robust, and accurate. In a leave-one-out validation on 54 normal young adults, the method yielded a mean Dice κ of 0.87 for the HC, 0.81 for the AG, 0.73 for the anterior parts of the parahippocampal gyrus (entorhinal and perirhinal cortex), and 0.73 for the posterior parahippocampal gyrus.
Keywords: appearance modeling; label fusion; medial temporal lobe structures; nonlocal means; segmentation.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A protocol for manual segmentation of medial temporal lobe subregions in 7 Tesla MRI.Neuroimage Clin. 2017 May 26;15:466-482. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2017.05.022. eCollection 2017. Neuroimage Clin. 2017. PMID: 28652965 Free PMC article.
-
Appearance-based modeling for segmentation of hippocampus and amygdala using multi-contrast MR imaging.Neuroimage. 2011 Sep 15;58(2):549-59. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.06.054. Epub 2011 Jun 25. Neuroimage. 2011. PMID: 21741485
-
Volumetric analysis of medial temporal lobe structures in brain development from childhood to adolescence.Neuroimage. 2013 Jul 1;74:276-87. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.02.032. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Neuroimage. 2013. PMID: 23485848
-
[Functional neuroimaging studies of episodic memory--functional dissociation in the medial temporal lobe structures].Brain Nerve. 2008 Jul;60(7):833-44. Brain Nerve. 2008. PMID: 18646623 Review. Japanese.
-
Imaging recollection and familiarity in the medial temporal lobe: a three-component model.Trends Cogn Sci. 2007 Sep;11(9):379-86. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2007.08.001. Epub 2007 Aug 17. Trends Cogn Sci. 2007. PMID: 17707683 Review.
Cited by
-
Local manifold learning for multiatlas segmentation: application to hippocampal segmentation in healthy population and Alzheimer's disease.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015 Oct;21(10):826-36. doi: 10.1111/cns.12415. Epub 2015 Jun 30. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015. PMID: 26122409 Free PMC article.
-
NEOCIVET: Towards accurate morphometry of neonatal gyrification and clinical applications in preterm newborns.Neuroimage. 2016 Sep;138:28-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.05.034. Epub 2016 May 13. Neuroimage. 2016. PMID: 27184202 Free PMC article.
-
Robust skull stripping using multiple MR image contrasts insensitive to pathology.Neuroimage. 2017 Feb 1;146:132-147. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.11.017. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Neuroimage. 2017. PMID: 27864083 Free PMC article.
-
Automated segmentation of medial temporal lobe subregions on in vivo T1-weighted MRI in early stages of Alzheimer's disease.Hum Brain Mapp. 2019 Aug 15;40(12):3431-3451. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24607. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Hum Brain Mapp. 2019. PMID: 31034738 Free PMC article.
-
Scoring by nonlocal image patch estimator for early detection of Alzheimer's disease.Neuroimage Clin. 2012 Oct 17;1(1):141-52. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2012.10.002. eCollection 2012. Neuroimage Clin. 2012. PMID: 24179747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aljabar P, Heckemann R, Hammers A, Hajnal JV, Rueckert D (2009): Multi‐atlas based segmentation of brain images: Atlas selection and its effect on accuracy. Neuroimage 46:726–738. - PubMed
-
- Babalola KO, Patenaude B, Aljabar P, Schnabel J, Kennedy D, Crum W, Smith S, Cootes T, Jenkinson M, Rueckert D (2009): An evaluation of four automatic methods of segmenting the subcortical structures in the brain. Neuroimage 47:1435–1447. - PubMed
-
- Baxter MG (2009): Involvement of medial temporal lobe structures in memory and perception. Neuron 61:667–677. - PubMed

