Type II p21-activated kinases (PAKs) are regulated by an autoinhibitory pseudosubstrate
- PMID: 22988085
- PMCID: PMC3479536
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1214447109
Type II p21-activated kinases (PAKs) are regulated by an autoinhibitory pseudosubstrate
Abstract
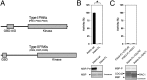
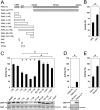
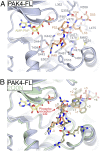
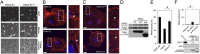
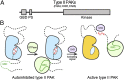
The type II p21-activated kinases (PAKs) are key effectors of RHO-family GTPases involved in cell motility, survival, and proliferation. Using a structure-guided approach, we discovered that type II PAKs are regulated by an N-terminal autoinhibitory pseudosubstrate motif centered on a critical proline residue, and that this regulation occurs independently of activation loop phosphorylation. We determined six X-ray crystal structures of either full-length PAK4 or its catalytic domain, that demonstrate the molecular basis for pseudosubstrate binding to the active state with phosphorylated activation loop. We show that full-length PAK4 is constitutively autoinhibited, but mutation of the pseudosubstrate releases this inhibition and causes increased phosphorylation of the apoptotic regulation protein Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L) antagonist causing cell death and cellular morphological changes. We also find that PAK6 is regulated by the pseudosubstrate region, indicating a common type II PAK autoregulatory mechanism. Finally, we find Src SH3, but not β-PIX SH3, can activate PAK4. We provide a unique understanding for type II PAK regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

