Calcium-activated chloride channel TMEM16A modulates mucin secretion and airway smooth muscle contraction
- PMID: 22988107
- PMCID: PMC3479591
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1214596109
Calcium-activated chloride channel TMEM16A modulates mucin secretion and airway smooth muscle contraction
Abstract
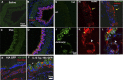
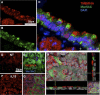
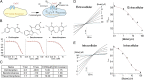
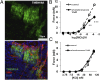
Mucous cell hyperplasia and airway smooth muscle (ASM) hyperresponsiveness are hallmark features of inflammatory airway diseases, including asthma. Here, we show that the recently identified calcium-activated chloride channel (CaCC) TMEM16A is expressed in the adult airway surface epithelium and ASM. The epithelial expression is increased in asthmatics, particularly in secretory cells. Based on this and the proposed functions of CaCC, we hypothesized that TMEM16A inhibitors would negatively regulate both epithelial mucin secretion and ASM contraction. We used a high-throughput screen to identify small-molecule blockers of TMEM16A-CaCC channels. We show that inhibition of TMEM16A-CaCC significantly impairs mucus secretion in primary human airway surface epithelial cells. Furthermore, inhibition of TMEM16A-CaCC significantly reduces mouse and human ASM contraction in response to cholinergic agonists. TMEM16A-CaCC blockers, including those identified here, may positively impact multiple causes of asthma symptoms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ferrera L, Caputo A, Galietta LJ. TMEM16A protein: A new identity for Ca(2+)-dependent Cl− channels. Physiology (Bethesda) 2010;25:357–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

