Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha-dependent induction of FoxP3 drives regulatory T-cell abundance and function during inflammatory hypoxia of the mucosa
- PMID: 22988108
- PMCID: PMC3478644
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1202366109
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha-dependent induction of FoxP3 drives regulatory T-cell abundance and function during inflammatory hypoxia of the mucosa
Abstract
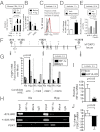
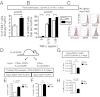
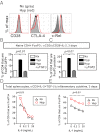
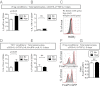
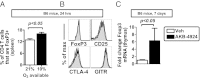
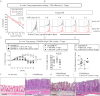
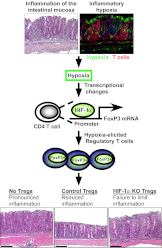
Recent studies have demonstrated dramatic shifts in metabolic supply-and-demand ratios during inflammation, a process resulting in localized tissue hypoxia within inflammatory lesions ("inflammatory hypoxia"). As part of the adaptive immune response, T cells are recruited to sites of inflammatory hypoxia. Given the profound effects of hypoxia on gene regulation, we hypothesized that T-cell differentiation is controlled by hypoxia. To pursue this hypothesis, we analyzed the transcriptional consequences of ambient hypoxia (1% oxygen) on a broad panel of T-cell differentiation factors. Surprisingly, these studies revealed selective, robust induction of FoxP3, a key transcriptional regulator for regulatory T cells (Tregs). Studies of promoter binding or loss- and gain-of-function implicated hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α in inducing FoxP3. Similarly, hypoxia enhanced Treg abundance in vitro and in vivo. Finally, Treg-intrinsic HIF-1α was required for optimal Treg function and Hif1a-deficient Tregs failed to control T-cell-mediated colitis. These studies demonstrate that hypoxia is an intrinsic molecular cue that promotes FoxP3 expression, in turn eliciting potent anti-inflammatory mechanisms to limit tissue damage in conditions of reduced oxygen availability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Semenza GL. Oxygen homeostasis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2010;2:336–361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK083385/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL098294/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL0921/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL60569/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL098294/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL060569/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK050189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK050189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK095491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK083385/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092188/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK50189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

