Science faculty's subtle gender biases favor male students
- PMID: 22988126
- PMCID: PMC3478626
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1211286109
Science faculty's subtle gender biases favor male students
Abstract
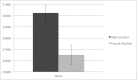
Despite efforts to recruit and retain more women, a stark gender disparity persists within academic science. Abundant research has demonstrated gender bias in many demographic groups, but has yet to experimentally investigate whether science faculty exhibit a bias against female students that could contribute to the gender disparity in academic science. In a randomized double-blind study (n = 127), science faculty from research-intensive universities rated the application materials of a student-who was randomly assigned either a male or female name-for a laboratory manager position. Faculty participants rated the male applicant as significantly more competent and hireable than the (identical) female applicant. These participants also selected a higher starting salary and offered more career mentoring to the male applicant. The gender of the faculty participants did not affect responses, such that female and male faculty were equally likely to exhibit bias against the female student. Mediation analyses indicated that the female student was less likely to be hired because she was viewed as less competent. We also assessed faculty participants' preexisting subtle bias against women using a standard instrument and found that preexisting subtle bias against women played a moderating role, such that subtle bias against women was associated with less support for the female student, but was unrelated to reactions to the male student. These results suggest that interventions addressing faculty gender bias might advance the goal of increasing the participation of women in science.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology (2012). Engage to excel: Producing one million additional college graduates with degrees in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. Available at http://www.whitehouse.gov/sites/default/files/microsites/ostp/pcast-enga.... (Accessed February 13, 2012)
-
- Handelsman J, et al. Careers in science. More women in science. Science. 2005;309:1190–1191. - PubMed
-
- United States National Academy of Sciences . Beyond Bias and Barriers: Fulfilling the Potential of Women in Academic Science and Engineering. Washington, DC: National Academies; 2007. - PubMed
-
- National Science Foundation . Women, Minorities, and Persons with Disabilities in Science and Engineering. Arlington: National Science Foundation; 2009.
-
- Bell N. Graduate Enrollment and Degrees: 1999 to 2009. Washington, DC: Council of Graduate Schools; 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

