A phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Pax3 axis regulates Brn-2 expression in melanoma
- PMID: 22988297
- PMCID: PMC3486186
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01067-12
A phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Pax3 axis regulates Brn-2 expression in melanoma
Abstract
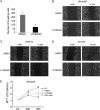
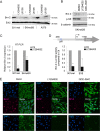
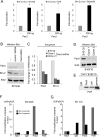
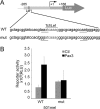
Deregulation of transcription arising from mutations in key signaling pathways is a hallmark of cancer. In melanoma, the most aggressive and lethal form of skin cancer, the Brn-2 transcription factor (POU3F2) regulates proliferation and invasiveness and lies downstream from mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and Wnt/β-catenin, two melanoma-associated signaling pathways. In vivo Brn-2 represses expression of the microphthalmia-associated transcription factor, MITF, to drive cells to a more stem cell-like and invasive phenotype. Given the key role of Brn-2 in regulating melanoma biology, understanding the signaling pathways that drive Brn-2 expression is an important issue. Here, we show that inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling reduces invasiveness of melanoma cells in culture and strongly inhibits Brn-2 expression. Pax3, a transcription factor regulating melanocyte lineage-specific genes, directly binds and regulates the Brn-2 promoter, and Pax3 expression is also decreased upon PI3K inhibition. Collectively, our results highlight a crucial role for PI3K in regulating Brn-2 and Pax3 expression, reveal a mechanism by which PI3K can regulate invasiveness, and imply that PI3K signaling is a key determinant of melanoma subpopulation diversity. Together with our previous work, the results presented here now place Brn-2 downstream of three melanoma-associated signaling pathways.
Figures

References
-
- Arozarena I, et al. 2011. Oncogenic BRAF induces melanoma cell invasion by downregulating the cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase PDE5A. Cancer Cell 19:45–57 - PubMed
-
- Boyle GM, et al. 2011. Melanoma cell invasiveness is regulated by miR-211 suppression of the BRN2 transcription factor. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 24:525–537 - PubMed
-
- Carreira S, et al. 2005. Mitf cooperates with Rb1 and activates p21Cip1 expression to regulate cell cycle progression. Nature 433:764–769 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
