Arecanut as an emerging etiology of oral cancers in India
- PMID: 22988348
- PMCID: PMC3439794
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-5851.99726
Arecanut as an emerging etiology of oral cancers in India
Abstract
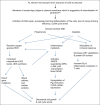
Arecanut (AN) usage is widespread in Asian countries, especially India and Taiwan. The incidence of oral cancer is increasing day by day, but there is no exponential increase with tobacco usage. Especially in the country like Taiwan where betel quid mostly do not contain tobacco, AN can be correlated with the increased incidence of cancer. There are different studies in the literature about AN and oral cancer but none of them have concluded with the definite pathway for carcinogenesis. The present paper includes reviews of the literature for AN and oral cancer and summarizes the possible mechanisms associated with AN-induced carcinogenesis; and we have also tried to propose pathway of carcinogenesis.
Keywords: Arecanut; Asian countries; betel quid; carcinogenesis; oral cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
References
-
- Gupta PC. Areca nut use in India. Indian J Med Sci. 2007;61:317–9. - PubMed
-
- Sharan RN. Association of betel nut with carcinogenesis: A review. Cancer J. 1996;9:13–19.
-
- Bobba R, Khan Y. Cancer in India – An Overview. GOR. 2003;5:93–6.
-
- Ray CS, Gupta PC, Beyer JD. Research on tobacco in India (including betel quid and areca nut)- An annotated bibliography of research on use, health effects, economics, and control efforts. 2003 Aug
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources