Podoplanin: emerging functions in development, the immune system, and cancer
- PMID: 22988448
- PMCID: PMC3439854
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00283
Podoplanin: emerging functions in development, the immune system, and cancer
Abstract
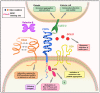
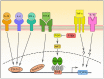
Podoplanin (PDPN) is a well-conserved, mucin-type transmembrane protein expressed in multiple tissues during ontogeny and in adult animals, including the brain, heart, kidney, lungs, osteoblasts, and lymphoid organs. Studies of PDPN-deficient mice have demonstrated that this molecule plays a critical role in development of the heart, lungs, and lymphatic system. PDPN is widely used as a marker for lymphatic endothelial cells and fibroblastic reticular cells of lymphoid organs and for lymphatics in the skin and tumor microenvironment. Much of the mechanistic insight into PDPN biology has been gleaned from studies of tumor cells; tumor cells often upregulate PDPN as they undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition and this upregulation is correlated with increased motility and metastasis. The physiological role of PDPN that has been most studied is its ability to aggregate and activate CLEC-2-expressing platelets, as PDPN is the only known endogenous ligand for CLEC-2. However, more recent studies have revealed that PDPN also plays crucial roles in the biology of immune cells, including T cells and dendritic cells. This review will provide a comprehensive overview of the diverse roles of PDPN in development, immunology, and cancer.
Keywords: CLEC-2; cancer-associated fibroblasts; lymph node stromal cells; lymphatic endothelial cells; platelets; podoplanin.
Figures
References
-
- Abtahian F., Guerriero A., Sebzda E., Lu M.-M., Zhou R., Mocsai A., Myers E. E., Huang B., Jackson D. G., Ferrari V. A., Tybulewicz V., Lowell C. A., Lepore J. J., Koretzky G. A., Kahn M. L. (2003). Regulation of blood and lymphatic vascular separation by signaling proteins SLP-76 and Syk. Science 299 247–251 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Acton S.E., Astarita J., Malhotra D., Luckacs-Kornek V., Franz B., Hess P., Jakus Z., Kuligowski M., Fletcher A., Elpek K., Bellemare-Pelletier A., Sceats L., Reynoso E., Gonzalez S., Graham D., Chang J., Peters A., Woodruff M., Kim Y., Swat W., Morita T., Kuchroo V., Carroll M., Kahn M., Wucherpfennig K., Turley S. (2012). Podoplanin-rich stromal networks induce dendritic cell motility via activation of C-type lectin receptor CLEC-2. Immunity 37 276–289 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barth K., Bläsche R., Kasper M. (2010). T1alpha/podoplanin shows raft-associated distribution in mouse lung alveolar epithelial E10 cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 25 103–112 - PubMed
-
- Bekiaris V., Withers D., Glanville S. H., Mcconnell F. M., Parnell S. M., Kim M.-Y., Gaspal F. M. C., Jenkinson E., Sweet C., Anderson G, Lane P. J. L. (2007). Role of CD30 in B/T segregation in the spleen. J. Immunol. 179 7535–7543 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

