Cellular programming and reprogramming: sculpting cell fate for the production of dopamine neurons for cell therapy
- PMID: 22988464
- PMCID: PMC3441013
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/412040
Cellular programming and reprogramming: sculpting cell fate for the production of dopamine neurons for cell therapy
Abstract
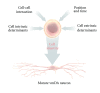
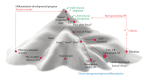
Pluripotent stem cells are regarded as a promising cell source to obtain human dopamine neurons in sufficient amounts and purity for cell replacement therapy. Importantly, the success of clinical applications depends on our ability to steer pluripotent stem cells towards the right neuronal identity. In Parkinson disease, the loss of dopamine neurons is more pronounced in the ventrolateral population that projects to the sensorimotor striatum. Because synapses are highly specific, only neurons with this precise identity will contribute, upon transplantation, to the synaptic reconstruction of the dorsal striatum. Thus, understanding the developmental cell program of the mesostriatal dopamine neurons is critical for the identification of the extrinsic signals and cell-intrinsic factors that instruct and, ultimately, determine cell identity. Here, we review how extrinsic signals and transcription factors act together during development to shape midbrain cell fates. Further, we discuss how these same factors can be applied in vitro to induce, select, and reprogram cells to the mesostriatal dopamine fate.
Figures

References
-
- Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rüb U, de Vos RAI, Jansen Steur ENH, Braak E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging. 2003;24(2):197–211. - PubMed
-
- Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H, Ohama E, Ikuta F. Parkinson’s disease: an immunohistochemical study of Lewy body-containing neurons in the enteric nervous system. Acta Neuropathologica. 1990;79(6):581–583. - PubMed
-
- Zimprich A, Biskup S, Leitner P, et al. Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant Parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron. 2004;44(4):601–607. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

