Efficacy of Boesenbergia rotunda Treatment against Thioacetamide-Induced Liver Cirrhosis in a Rat Model
- PMID: 22988470
- PMCID: PMC3439995
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/137083
Efficacy of Boesenbergia rotunda Treatment against Thioacetamide-Induced Liver Cirrhosis in a Rat Model
Abstract
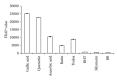
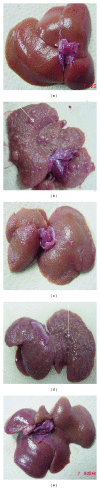
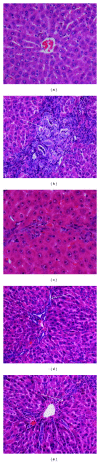
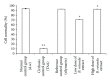
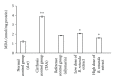
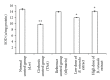
Background. Experimental research in hepatology has focused on developing traditional medicines into potential pharmacological solutions aimed at protecting liver from cirrhosis. Along the same line, this study investigated the effects of ethanol-based extract from a traditional medicine plant Boesenbergia rotunda (BR) on liver cirrhosis. Methodology/Results. The BR extract was tested for toxicity on 3 groups of rats subjected to vehicle (10% Tween 20, 5 mL/kg) and 2g/kg and 5g/kg doses of the extract, respectively. Next, experiments were conducted on a rat model of cirrhosis induced by thioacetamide injection. The rats were divided into five groups and, respectively, administered orally with 10% Tween-20 (5 mL/kg) (normal control group), 10% Tween-20 (5 mL/kg) (cirrhosis control group), 50 mg/kg of silymarin (reference control group), and 250 mg/kg and 500 mg/kg of BR extract (experimental groups) daily for 8 weeks. The rats in normal group were intraperitoneally injected with sterile distilled water (1 mL/kg) 3 times/week, and those in the remaining groups were injected intraperitoneally with thioacetamide (200 mg/kg) thrice weekly. At the end of the 8 weeks, the animals were sacrificed and samples were collected for comprehensive histopathological, coagulation profile and biochemical evaluations. Also, the antioxidant activity of the BR extract was determined and compared with that of silymarin. Data from the acute toxicity tests showed that the extract was safe to use. Histological analysis of the livers of the rats in cirrhosis control group revealed uniform coarse granules on their surfaces, hepatocytic necrosis, and lymphocytes infiltration. But, the surfaces morphologically looked much smoother and the cell damage was much lesser in those livers from the normal control, silymarin and BR-treated groups. In the high-dose BR treatment group, the livers of the rats exhibited nearly normal looking lobular architecture, minimal inflammation, and minimal hepatocyte damage, the levels of the serum biomarkers and liver enzymes read nearly normal, and these results were all comparable to those observed or quantified from the normal and silymarin-treated groups. The BR extract had the antioxidant activity about half of what was recorded for silymarin. Conclusion. The progression of the liver cirrhosis can be intervened using the ethanol-based BR extract, and the liver's status quo of property, structure, and function can be preserved. This capability of the extract warrants further studies exploring the significance of its pharmacologic potential in successfully treating the liver cirrhosis in humans.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protective Role of Phyllanthus niruri Extract against Thioacetamide-Induced Liver Cirrhosis in Rat Model.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:241583. doi: 10.1155/2012/241583. Epub 2012 May 10. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012. PMID: 22649471 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo hepatoprotective effect of Morinda elliptica stem extract against liver fibrosis induced by thioacetamide.Environ Toxicol. 2021 Dec;36(12):2404-2413. doi: 10.1002/tox.23353. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Environ Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34436826
-
Mechanism of Hepatoprotective Effect of Boesenbergia rotunda in Thioacetamide-Induced Liver Damage in Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:157456. doi: 10.1155/2013/157456. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Jul 18;2018:1072403. doi: 10.1155/2018/1072403. PMID: 23997791 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Final report on the safety assessment of capsicum annuum extract, capsicum annuum fruit extract, capsicum annuum resin, capsicum annuum fruit powder, capsicum frutescens fruit, capsicum frutescens fruit extract, capsicum frutescens resin, and capsaicin.Int J Toxicol. 2007;26 Suppl 1:3-106. doi: 10.1080/10915810601163939. Int J Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17365137 Review.
-
Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of milk thistle extract (CAS No. 84604-20-6) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (Feed Studies).Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2011 May;(565):1-177. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2011. PMID: 21685957 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-ulcerogenic effect of methanolic extracts from Enicosanthellum pulchrum (King) Heusden against ethanol-induced acute gastric lesion in animal models.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 7;9(11):e111925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111925. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2023 Nov 10;18(11):e0294008. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294008. PMID: 25379712 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
In vivo evaluation of ethanolic extract of Zingiber officinale rhizomes for its protective effect against liver cirrhosis.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:918460. doi: 10.1155/2013/918460. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24396831 Free PMC article.
-
Oral sub-chronic toxicity of fingerroot (Boesenbergia rotunda) rhizome extract formulation in Wistar rats.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Jan 30;12:224-233. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.01.013. eCollection 2024 Jun. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38328737 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective effects of methanolic extract of green tea against Thioacetamide-Induced liver injury in Sprague Dawley rats.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan;29(1):564-573. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.023. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35002452 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional usages, chemical metabolites, pharmacological activities, and pharmacokinetics of Boesenbergia rotunda (L.) Mansf.: a comprehensive review.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 19;16:1527210. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1527210. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40176912 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yang H, Sung SH, Kim YC. Two new hepatoprotective stilbene glycosides from Acer mono leaves. Journal of Natural Products. 2005;68(1):101–103. - PubMed
-
- Wang N, Li P, Wang Y, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of Hypericum japonicum extract and its fractions. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2008;116(1):1–6. - PubMed
-
- El-Abhar HS, Hammad LNA, Gawad HSA. Modulating effect of ginger extract on rats with ulcerative colitis. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2008;118(3):367–372. - PubMed
-
- Shindo K, Kato M, Kinoshita A, Kobayashi A, Koike Y. Analysis of antioxidant activities contained in the Boesenbergia pandurata Schult. rhizome. Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry. 2006;70(9):2281–2284. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

