Site-isolated redox reactivity in a trinuclear iron complex
- PMID: 22988949
- PMCID: PMC3464975
- DOI: 10.1021/ic301241s
Site-isolated redox reactivity in a trinuclear iron complex
Abstract
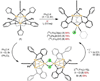
The symmetric, high-spin triiron complex ((Ph)L)Fe(3)(THF)(3) reacts with mild chemical oxidants (e.g., Ph(3)C-X, I(2)) to afford an asymmetric core, where one iron bears the halide ligand ((Ph)L)Fe(3)X(L) and the hexadentate ((Ph)L = MeC(CH(2)NPh-o-NPh)(3)) ligand has undergone significant rearrangement. In the absence of a suitable trapping ligand, the chlorine and bromine complexes form (μ-X)(2)-bridged structures of the type [((Ph)L)Fe(3)(μ-X)](2). In the trinuclear complexes, the halide-bearing iron site sits in approximate trigonal-bipyramidal (tbp) geometry, formed by two ((Ph)L) anilides and an exogenous solvent molecule. The two distal iron atoms reside in distorted square-planar sites featuring a short Fe-Fe separation at 2.301 Å, whereas the distance to the tbp site is substantially elongated (2.6-2.7 Å). Zero-field, (57)Fe Mössbauer analysis reveals the diiron unit as the locus of oxidation, while the tbp site bearing the halide ligand remains divalent. Magnetic data acquired for the series reveal that the oxidized diiron unit comprises a strongly coupled S = (3)/(2) unit that is weakly ferromagnetically coupled to the high-spin (S = 2) ferrous site, giving an overall S = (7)/(2) ground state for the trinuclear units.
Figures
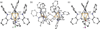

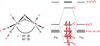
References
-
-
Nitrogenase: Burgess BK, Lowe DJ. Chem. Rev. 1996;96:2983–3012. Dos Santos PC, Igarashi RY, Lee HI, Hoffman BM, Seefeldt LC, Dean DR. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005;38:208–214. Hoffman BM, Dean DR, Seefeldt LC. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009;42:609–619. Photosystem II: Nugent J, editor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2001;1503:1. Ferreira KN, Iverson TM, Maghlaoui K, Barber J, Iwata S. Science. 2004;303:1831. Iwata S, Barber J. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2004;14:447. N2O reductase: Brown K, Djinovic-Carugo K, Haltia T, Cabrito I, Saraste M, Moura JJG, Moura I, Tegoni M, Cambillau C. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:41133. Brown K, Tegoni M, Prudêncio M, Pereira AS, Besson S, Moura JJ, Moura I, Cambillau C. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000;7:191. Chen P, George SD, Cabrito I, Antholine WE, Moura JG, Moura I, Hedman B, Hodgson KO, Solomon EI. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002;124:744.
-
-
- Zhao Q, Betley TA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. . 2011;50:709–712. - PubMed
- Powers TM, Fout AR, Zheng SL, Betley TA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011;133:3336. - PMC - PubMed
- Zhao Q, Harris TD, Betley TA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011;133:8293. - PubMed
- Harris TD, Zhao Q, Hernández Sánchez R, Betley TA. Chem. Commun. 2011;47:6344. - PubMed
- Harris TD, Betley TA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011;133:13852. - PubMed
- Fout AR, Zhao Q, Xiao DJ, Betley TA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011;133:16750. - PMC - PubMed
- Eames EV, Harris TD, Betley TA. Chem. Sci. 2012;3:407.
-
- Adams RD. J. Organometallic Chem. 2000;600:1–6.
- Suzuki H. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2002:1009–1023.
- Dyson PJ. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2004;248:2443–2458.
- Pap JS, DeBeer George S, Berry JF. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008;47:10102–10105. - PubMed
-
- Gomberg M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1900;22:757.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

