Arsenic trioxide-induced growth arrest of breast cancer MCF-7 cells involving FOXO3a and IκB kinase β expression and localization
- PMID: 22988968
- PMCID: PMC3466909
- DOI: 10.1089/cbr.2012.1162
Arsenic trioxide-induced growth arrest of breast cancer MCF-7 cells involving FOXO3a and IκB kinase β expression and localization
Abstract
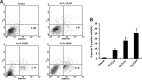
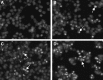
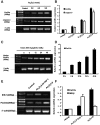
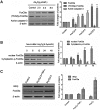
Currently, arsenic has been clinically investigated as a therapeutic agent for a variety of solid malignancies, including breast cancer. However, the exact underlying molecular mechanisms through which arsenic trioxide (As(2)O(3)) induces cell growth arrest and apoptosis in solid tumors have not been clearly understood. The aim of our study was to gain an insight into the effect of As(2)O(3) on the human breast cancer MCF-7 cell line and investigate cell growth inhibition, apoptosis, and the molecular mechanism after As(2)O(3) treatment in MCF-7 cells. Expression of FOXO3a, nuclear-FOXO3a, caspase-3, and IκB kinase β (IKKβ) mRNA levels in MCF-7 cells was determined by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The protein expression was examined by the Western blot analysis and immunocytochemical staining. The distribution of apoptotic cells was assessed by flow cytometry, and the morphology of the apoptotic cells was investigated by Hoechest33258 staining. Our results showed that As(2)O(3) significantly induced the apoptosis of MCF-7 cells tested in this study in a dose-dependent manner. As(2)O(3) induced the decrease of IKKβ expression and the increase of total as well as nuclear FOXO3a expression, which triggered the phosphorylation of cytoplasmic FOXO3a at the Thr32 residue decrease. RT-PCR, Western blot analysis, and immunocytochemistry revealed that the expression of IKKβ in MCF-7 cells was upregulated when As(2)O(3) was combined with tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), whereas the expression of FOXO3a was downregulated in comparison with the As(2)O(3)-alone group. These findings indicated a specific molecular mechanism by which MCF-7 cell lines were susceptible to the As(2)O(3) therapy through FOXO3a expression and localization. This FOXO3a accumulation may be well correlated with the As(2)O(3)-induced reduction of active IKKβ, which may provide new insights into As(2)O(3)-related signaling activities.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Arsenic trioxide-induced growth arrest of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells involving FOXO3a expression and localization.Med Oncol. 2009;26(2):178-85. doi: 10.1007/s12032-008-9105-8. Epub 2008 Oct 21. Med Oncol. 2009. PMID: 18937079
-
TG-interacting factor transcriptionally induced by AKT/FOXO3A is a negative regulator that antagonizes arsenic trioxide-induced cancer cell apoptosis.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015 May 15;285(1):41-50. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2015.03.007. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25791921
-
Arsenic trioxide causes redistribution of cell cycle, caspase activation, and GADD expression in human colonic, breast, and pancreatic cancer cells.Cancer Invest. 2004;22(3):389-400. doi: 10.1081/cnv-200029068. Cancer Invest. 2004. PMID: 15493360
-
Arsenic-induced apoptosis in malignant cells in vitro.Leuk Lymphoma. 2000 Mar;37(1-2):53-63. doi: 10.3109/10428190009057628. Leuk Lymphoma. 2000. PMID: 10721769 Review.
-
Role and regulation of FOXO3a: new insights into breast cancer therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 4;15:1346745. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1346745. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38505423 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differentiation induction of human breast cancer cells by arsenite in combination with tetrandrine.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Dec 15;11(12):7310-7323. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31934280 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for Chemical Contributions to Breast Cancer Risk: A Case Study for Chemical Safety Evaluation.Environ Health Perspect. 2015 Dec;123(12):1255-64. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1408337. Epub 2015 Jun 2. Environ Health Perspect. 2015. PMID: 26032647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Survivin Splice Variants in Arsenic Trioxide (As₂O₃)-Induced Deactivation of PI3K and MAPK Cell Signalling Pathways in MCF-7 Cells.Genes (Basel). 2019 Jan 14;10(1):41. doi: 10.3390/genes10010041. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30646589 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor activity of arsenite in combination with tetrandrine against human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 in vitro and in vivo.Cancer Cell Int. 2018 Aug 13;18:113. doi: 10.1186/s12935-018-0613-0. eCollection 2018. Cancer Cell Int. 2018. PMID: 30123091 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenic Trioxide Suppressed Migration and Angiogenesis by Targeting FOXO3a in Gastric Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 24;19(12):3739. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123739. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30477221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Evens AM. Tallman MS. Gartenhaus RB. The potential of arsenic trioxide in the treatment of malignant disease: Past, present, and future. Leuk Res. 2004;28:891. - PubMed
-
- Ye J. Li A. Liu Q, et al. Inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase enhances apoptosis induced by arsenic trioxide in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2005;32:1042. - PubMed
-
- Chow SK. Chan JY. Fung KP. Inhibition of cell proliferation and the action mechanisms of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) on human breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 2004;93:173. - PubMed
-
- Weigel D. Jürgens G. Küttner F, et al. The homeotic gene fork head encodes a nuclear protein and is expressed in the terminal regions of the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989;57:645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

