An efficient RNA interference screening strategy for gene functional analysis
- PMID: 22988976
- PMCID: PMC3533828
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-491
An efficient RNA interference screening strategy for gene functional analysis
Abstract
Background: RNA interference (RNAi) is commonly applied in genome-scale gene functional screens. However, a one-on-one RNAi analysis that targets each gene is cost-ineffective and laborious. Previous studies have indicated that siRNAs can also affect RNAs that are near-perfectly complementary, and this phenomenon has been termed an off-target effect. This phenomenon implies that it is possible to silence several genes simultaneously with a carefully designed siRNA.
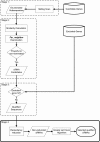
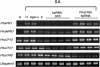
Results: We propose a strategy that is combined with a heuristic algorithm to design suitable siRNAs that can target multiple genes and a group testing method that would reduce the number of required RNAi experiments in a large-scale RNAi analysis. To verify the efficacy of our strategy, we used the Orchid expressed sequence tag data as a case study to screen the putative transcription factors that are involved in plant disease responses. According to our computation, 94 qualified siRNAs were sufficient to examine all of the predicated 229 transcription factors. In addition, among the 94 computer-designed siRNAs, an siRNA that targets both TF15 (a previously identified transcription factor that is involved in the plant disease-response pathway) and TF21 was introduced into orchids. The experimental results showed that this siRNA can simultaneously silence TF15 and TF21, and application of our strategy successfully confirmed that TF15 is involved in plant defense responses. Interestingly, our second-round analysis, which used an siRNA specific to TF21, indicated that TF21 is a previously unidentified transcription factor that is related to plant defense responses.
Conclusions: Our computational results showed that it is possible to screen all genes with fewer experiments than would be required for the traditional one-on-one RNAi screening. We also verified that our strategy is capable of identifying genes that are involved in a specific phenotype.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A computational model for compressed sensing RNAi cellular screening.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 Dec 27;13:337. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-337. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 23270311 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting fungal genes by diced siRNAs: a rapid tool to decipher gene function in Aspergillus nidulans.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 10;8(10):e75443. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075443. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24130711 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of leafbladeless1-regulated and phased small RNAs underscores the importance of the TAS3 ta-siRNA pathway to maize development.PLoS Genet. 2014 Dec 11;10(12):e1004826. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004826. eCollection 2014 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 25503246 Free PMC article.
-
Inputs and outputs for chromatin-targeted RNAi.Trends Plant Sci. 2008 Jul;13(7):383-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.05.001. Epub 2008 Jun 10. Trends Plant Sci. 2008. PMID: 18550415 Review.
-
Recent advances in plant-virus interaction with emphasis on small interfering RNAs (siRNAs).Mol Biotechnol. 2013 Sep;55(1):63-77. doi: 10.1007/s12033-012-9615-7. Mol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23086491 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Autophagy in the Pine Wood Nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and the Molecular Characterization and Functional Analysis of Two Novel Autophagy-Related Genes, BxATG1 and BxATG8.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Mar 3;17(3):279. doi: 10.3390/ijms17030279. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26950119 Free PMC article.
-
De novo transcriptome and small RNA analysis of two Chinese willow cultivars reveals stress response genes in Salix matsudana.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 2;9(10):e109122. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109122. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25275458 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Profiling of Autophagy Genes BxATG1 and BxATG8 under Biotic and Abiotic Stresses in Pine Wood Nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Dec 6;18(12):2639. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122639. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29211016 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization and Functional Analysis of Three Autophagy Genes, BxATG5, BxATG9, and BxATG16, in Bursaphelenchus xylophilus.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 1;20(15):3769. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153769. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31374896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bennetzen JL, Kellogg EA, Lee M, Messing J. A plant genome initiative. Plant Cell. 1998;10:488–493.
-
- Dong Y, Burch-Smith TM, Liu Y, Mamillapalli P, Dinesh-Kumar SP. A ligation-independent cloning tobacco rattle virus vector for high-throughput virus-induced gene silencing identifies roles for NbMADS4-1 and -2 in floral development. Plant Physiol. 2007;145:1161–1170. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.107391. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gill BS, Appels R, Botha-Oberholster AM, Buell CR, Bennetzen JL, Chalhoub B, Chumley F, Dvorak J, Iwanaga M, Keller B. et al.A workshop report on wheat genome sequencing: international genome research on wheat consortium. Genetics. 2004;168:1087–1096. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.034769. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

