Crizotinib for the treatment of ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer: a success story to usher in the second decade of molecular targeted therapy in oncology
- PMID: 22989574
- PMCID: PMC3500356
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0311
Crizotinib for the treatment of ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer: a success story to usher in the second decade of molecular targeted therapy in oncology
Abstract
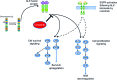
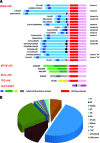
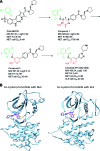
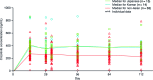
Crizotinib, an ALK/MET/ROS1 inhibitor, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in August 2011, merely 4 years after the first publication of ALK-rearranged NSCLC. The crizotinib approval was accompanied by the simultaneous approval of an ALK companion diagnostic fluorescent in situ hybridization assay for the detection of ALK-rearranged NSCLC. Crizotinib continued to be developed as an ALK and MET inhibitor in other tumor types driven by alteration in ALK and MET. Crizotinib has recently been shown to be an effective ROS1 inhibitor in ROS1-rearranged NSCLC, with potential future clinical applications in ROS1-rearranged tumors. Here we summarize the heterogeneity within the ALK- and ROS1-rearranged molecular subtypes of NSCLC. We review the past and future clinical development of crizotinib for ALK-rearranged NSCLC and the diagnostic assays to detect ALK-rearranged NSCLC. We highlight how the success of crizotinib has changed the paradigm of future drug development for targeted therapies by targeting a molecular-defined subtype of NSCLC despite its rarity and affected the practice of personalized medicine in oncology, emphasizing close collaboration between clinical oncologists, pathologists, and translational scientists.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
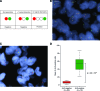
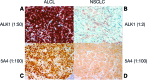
References
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Cohen MH, Williams GA, Sridhara R, et al. United States Food and Drug Administration Drug Approval summary: Gefitinib (ZD1839; Iressa) tablets. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:1212–1218. - PubMed
-
- Johnson JR, Cohen M, Sridhara R, et al. Approval summary for erlotinib for treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer after failure of at least one prior chemotherapy regimen. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:6414–6421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

