Involvement of calmodulin and calmodulin kinase II in tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced survival of bone marrow derived macrophages
- PMID: 22989752
- PMCID: PMC3485643
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.09.038
Involvement of calmodulin and calmodulin kinase II in tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced survival of bone marrow derived macrophages
Abstract
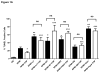
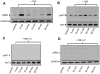
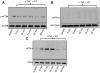
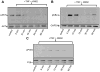
We previously showed that survival signaling in TNFα-treated, human THP1-derived macrophages (TDMs) has an obligatory requirement for constitutive Ca(2+) influx through a mechanism involving calmodulin/calmodulin kinase II (CAM/CAMKII). We also demonstrated that such requirement also applies to the protective actions of TNFα in murine bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) and that TRPC3 channels mediate constitutive Ca(2+) influx. Using a pharmacological approach we here examined if in BMDMs, similarly to TDMs, TNFα-induced survival signaling also involves CAM/CAMKII. In BMDMs, TNFα induced rapid activation of the survival pathways NFκB, AKT and p38MAPK. All these routes were activated in a PI3K-dependent fashion. Activation of AKT and NFκB, but not that of p38MAPK, was abrogated by the CAM inhibitor W7, while KN-62, a CAMKII inhibitor, prevented activation of AKT and p38MAPK but not that of NFκB. Inhibition of CAM or CAMKII completely prevented the protective actions of TNFα. Our observations indicate that in BMDMs CAM and CAMKII have differential contributions to the components of TNFα-dependent survival signaling and underscore a complex interplay among canonical survival routes. These findings set a signaling framework to understand how constitutive Ca(2+) influx couples to macrophage survival in BMDMs.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Gentili C, Picotto G, Morelli S, Boland R, de Boland AR. Effect of ageing in the early biochemical signals elicited by PTH in intestinal cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research. 2003;1593:169–178. - PubMed
-
- Sameermahmood Z, Balasubramanyam M, Saravanan T, Rema M. Curcumin Modulates SDF-1α/CXCR4–Induced Migration of Human Retinal Endothelial Cells (HRECs) Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 2008;49:3305–3311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

