P-value-based regulatory motif discovery using positional weight matrices
- PMID: 22990209
- PMCID: PMC3530678
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.139881.112
P-value-based regulatory motif discovery using positional weight matrices
Abstract
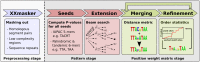
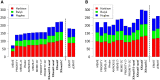
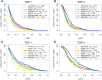
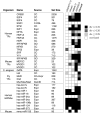
To analyze gene regulatory networks, the sequence-dependent DNA/RNA binding affinities of proteins and noncoding RNAs are crucial. Often, these are deduced from sets of sequences enriched in factor binding sites. Two classes of computational approaches exist. The first describe binding motifs by sequence patterns and search the patterns with highest statistical significance for enrichment. The second class uses the more powerful position weight matrices (PWMs). Instead of maximizing the statistical significance of enrichment, they maximize a likelihood. Here we present XXmotif (eXhaustive evaluation of matriX motifs), the first PWM-based motif discovery method that can optimize PWMs by directly minimizing their P-values of enrichment. Optimization requires computing millions of enrichment P-values for thousands of PWMs. For a given PWM, the enrichment P-value is calculated efficiently from the match P-values of all possible motif placements in the input sequences using order statistics. The approach can naturally combine P-values for motif enrichment, conservation, and localization. On ChIP-chip/seq, miRNA knock-down, and coexpression data sets from yeast and metazoans, XXmotif outperformed state-of-the-art tools, both in numbers of correctly identified motifs and in the quality of PWMs. In segmentation modules of D. melanogaster, we detect the known key regulators and several new motifs. In human core promoters, XXmotif reports most previously described and eight novel motifs sharply peaked around the transcription start site, among them an Initiator motif similar to the fly and yeast versions. XXmotif's sensitivity, reliability, and usability will help to leverage the quickly accumulating wealth of functional genomics data.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The XXmotif web server for eXhaustive, weight matriX-based motif discovery in nucleotide sequences.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jul;40(Web Server issue):W104-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks602. Epub 2012 Jun 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22693218 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized position weight matrices in prediction of novel putative binding sites for transcription factors in the Drosophila melanogaster genome.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 6;8(8):e68712. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068712. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23936309 Free PMC article.
-
abc4pwm: affinity based clustering for position weight matrices in applications of DNA sequence analysis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Mar 3;23(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-04615-z. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 35240993 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Motif Databases and Their Uses.Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2015 Sep 3;51:2.15.1-2.15.6. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi0215s51. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26334922 Review.
-
Analysis of Genomic Sequence Motifs for Deciphering Transcription Factor Binding and Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotic Cells.Front Genet. 2016 Feb 23;7:24. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00024. eCollection 2016. Front Genet. 2016. PMID: 26941778 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ProSampler: an ultrafast and accurate motif finder in large ChIP-seq datasets for combinatory motif discovery.Bioinformatics. 2019 Nov 1;35(22):4632-4639. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz290. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31070745 Free PMC article.
-
Bayesian Markov models consistently outperform PWMs at predicting motifs in nucleotide sequences.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jul 27;44(13):6055-69. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw521. Epub 2016 Jun 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27288444 Free PMC article.
-
Structural remodeling of AAA+ ATPase p97 by adaptor protein ASPL facilitates posttranslational methylation by METTL21D.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jan 24;120(4):e2208941120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2208941120. Epub 2023 Jan 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36656859 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing deep learning methods in cis-regulatory motif finding based on genomic sequencing data.Brief Bioinform. 2022 Jan 17;23(1):bbab374. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab374. Brief Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 34607350 Free PMC article.
-
The APT complex is involved in non-coding RNA transcription and is distinct from CPF.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Nov 30;46(21):11528-11538. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky845. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30247719 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailey TL, Elkan C 1994. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol 2: 28–36 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
