Phase I trial of axitinib combined with platinum doublets in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and other solid tumours
- PMID: 22990652
- PMCID: PMC3494447
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2012.406
Phase I trial of axitinib combined with platinum doublets in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and other solid tumours
Abstract
Background: This phase I dose-finding trial evaluated safety, efficacy and pharmacokinetics of axitinib, a potent and selective second-generation inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors, combined with platinum doublets in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and other solid tumours.
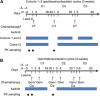
Methods: In all, 49 patients received axitinib 5 mg twice daily (b.i.d.) with paclitaxel/carboplatin or gemcitabine/cisplatin in 3-week cycles. Following determination of the maximum tolerated dose, a squamous cell NSCLC expansion cohort was enroled and received axitinib 5 mg b.i.d. with paclitaxel/carboplatin.
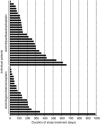
Results: Two patients experienced dose-limiting toxicities: febrile neutropenia (n=1) in the paclitaxel/carboplatin cohort and fatigue (n=1) in the gemcitabine/cisplatin cohort. Common nonhaematologic treatment-related adverse events were hypertension (36.7%), diarrhoea (34.7%) and fatigue (28.6%). No grade ≥3 haemoptysis occurred among 12 patients with squamous cell NSCLC. The objective response rate was 37.0% for patients receiving axitinib/paclitaxel/carboplatin (n=27) and 23.8% for patients receiving axitinib/gemcitabine/cisplatin (n=21). Pharmacokinetics of axitinib and chemotherapeutic agents were similar when administered alone or in combination.
Conclusion: Axitinib 5 mg b.i.d. may be combined with standard paclitaxel/carboplatin or gemcitabine/cisplatin regimens without evidence of overt drug-drug interactions. Both combinations demonstrated clinical efficacy and were well tolerated.
Figures
References
-
- Berns EM, Klijn JG, Look MP, Grebenchtchikov N, Vossen R, Peters H, Geurts-Moespot A, Portengen H, van Staveren IL, Meijer-van Gelder ME, Bakker B, Sweep FC, Foekens JA (2003) Combined vascular endothelial growth factor and TP53 status predicts poor response to tamoxifen therapy in estrogen receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 9: 1253–1258 - PubMed
-
- Burris HA (2009) Shortcomings of current therapies for non-small-cell lung cancer: unmet medical needs. Oncogene 28(Suppl 1): S4–S13 - PubMed
-
- Cohen EE, Rosen LS, Vokes EE, Kies MS, Forastiere AA, Worden FP, Kane MA, Sherman E, Kim S, Bycott P, Tortorici M, Shalinsky DR, Liau KF, Cohen RB (2008) Axitinib is an active treatment for all histologic subtypes of advanced thyroid cancer: results from a phase II study. J Clin Oncol 26: 4708–4713 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duffull SB, Robinson BA (1997) Clinical pharmacokinetics and dose optimisation of carboplatin. Clin Pharmacokinet 33: 161–183 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

