From IL-2 to IL-37: the expanding spectrum of anti-inflammatory cytokines
- PMID: 22990890
- PMCID: PMC3609707
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2406
From IL-2 to IL-37: the expanding spectrum of anti-inflammatory cytokines
Abstract
Feedback regulatory circuits provided by regulatory T cells (T(reg) cells) and suppressive cytokines are an intrinsic part of the immune system, along with effector functions. Here we discuss some of the regulatory cytokines that have evolved to permit tolerance to components of self as well as the eradication of pathogens with minimal collateral damage to the host. Interleukin 2 (IL-2), IL-10 and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) are well characterized, whereas IL-27, IL-35 and IL-37 represent newcomers to the spectrum of anti-inflammatory cytokines. We also emphasize how information accumulated through in vitro as well as in vivo studies of genetically engineered mice can help in the understanding and treatment of human diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
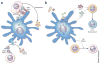
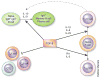
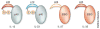
References
-
- Maloy KJ, Powrie F. Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2011;474:298–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

