PhosphdiesteRasE-5 Inhibition to Improve CLinical Status and EXercise Capacity in Diastolic Heart Failure (RELAX) trial: rationale and design
- PMID: 22991405
- PMCID: PMC3530955
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.112.969071
PhosphdiesteRasE-5 Inhibition to Improve CLinical Status and EXercise Capacity in Diastolic Heart Failure (RELAX) trial: rationale and design
Abstract
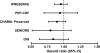
Heart failure (HF) with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) or “diastolic HF” accounts for approximately half of HF cases. To date, neurohumoral antagonists have failed to show a significant benefit on clinical outcomes in HFpEF. While our understanding of the pathophysiology of HFpEF continues to develop, multiple therapeutic targets have been identified in HFpEF which may be modifiable by augmentation of the intracellular second messenger cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) via phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition (PDE5I) in HFpEF. The PhosphodiesteRasE-5 Inhibition to Improve CLinical Status And EXercise Capacity in Diastolic Heart Failure (RELAX trial;
Figures
References
-
- Owan TE, Hodge DO, Herges RM, Jacobsen SJ, Roger VL, Redfield MM. Trends in prevalence and outcome of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. New Engl J Med. 2006;355:251–259. - PubMed
-
- Shah RV, Desai AS, Givertz MM. The effect of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors on mortality and heart failure hospitalization in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Card Fail. 2010;16:260–267. - PubMed
-
- van Veldhuisen DJ, Cohen-Solal A, Bohm M, Anker SD, Babalis D, Roughton M, Coats AJ, Poole-Wilson PA, Flather MD. Beta-blockade with nebivolol in elderly heart failure patients with impaired and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction: Data from seniors (study of effects of nebivolol intervention on outcomes and rehospitalization in seniors with heart failure) J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53:2150–2158. - PubMed
-
- Kitzman DW, Higginbotham MB, Cobb FR, Sheikh KH, Sullivan MJ. Exercise intolerance in patients with heart failure and preserved left ventricular systolic function: Failure of the frank-starling mechanism. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1991;17:1065–1072. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01 HL084890/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL084899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL084931/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL084891/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL07111-83/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007111/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL084907/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL084904/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL084931/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL084861/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024150/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL084890/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL084891/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL084875/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL084877/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL084861/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL084904/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL084904/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL084875/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105418/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL084889/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL084907/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL084899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL084877/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL084889/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

