The P granule component PGL-1 promotes the localization and silencing activity of the PUF protein FBF-2 in germline stem cells
- PMID: 22991439
- PMCID: PMC3445306
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.083980
The P granule component PGL-1 promotes the localization and silencing activity of the PUF protein FBF-2 in germline stem cells
Abstract
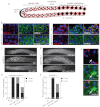
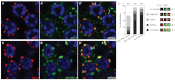
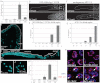
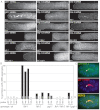
In the C. elegans germline, maintenance of undifferentiated stem cells depends on the PUF family RNA-binding proteins FBF-1 and FBF-2. FBF-1 and FBF-2 are 89% identical and are required redundantly to silence the expression of mRNAs that promote meiosis. Here we show that, despite their extensive sequence similarity, FBF-1 and FBF-2 have different effects on target mRNAs. FBF-1 promotes the degradation and/or transport of meiotic mRNAs out of the stem cell region, whereas FBF-2 prevents translation. FBF-2 activity depends on the P granule component PGL-1. PGL-1 is required to localize FBF-2 to perinuclear P granules and for efficient binding of FBF-2 to its mRNA targets. We conclude that multiple regulatory mechanisms converge on meiotic RNAs to ensure silencing in germline stem cells. Our findings also support the view that P granules facilitate mRNA silencing by providing an environment in which translational repressors can encounter their mRNA targets immediately upon exit from the nucleus.
Figures

References
-
- Crittenden S. L., Bernstein D. S., Bachorik J. L., Thompson B. E., Gallegos M., Petcherski A. G., Moulder G., Barstead R., Wickens M., Kimble J. (2002). A conserved RNA-binding protein controls germline stem cells in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 417, 660-663 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

