Ameliorative Effects of Scopoletin from Crossostephium chinensis against Inflammation Pain and Its Mechanisms in Mice
- PMID: 22991572
- PMCID: PMC3443580
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/595603
Ameliorative Effects of Scopoletin from Crossostephium chinensis against Inflammation Pain and Its Mechanisms in Mice
Abstract
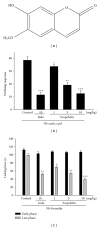
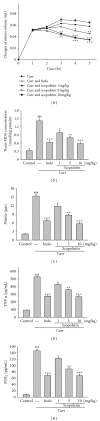
Scopoletin exists in nature as an anti-oxidant, hepatoprotective, and anti-inflammatory activities reagent. In this study, we have investigated the analgesic effects of the scopoletin using the models of acetic acid-induced writhing response and the formalin test, the anti-inflammatory effects of scopoletin using model of λ-carrageenan (Carr)-induced paw edema. The treatment of ICR mice with scopoletin inhibited the numbers of writhing response and the formalin-induced pain in the late phase. This study demonstrated that the administration of scopoletin resulted in the reduction of Carr-induced mice edema, and it increased the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) after Carr injection. We also demonstrated scopoletin significantly attenuated the malondialdehyde (MDA) level in the edema paw after Carr injection. Scopoletin decreased the NO, tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE(2)) levels on serum after Carr injection. Scopoletin decreased Carr-induced inducible NO synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expressions in the edema paw. These anti-inflammatory mechanisms of scopoletin might be related to the decrease in the level of MDA via increasing the activities of SOD, CAT, and GPx in the edema paw. Also, scopoletin could affect the production of NO, TNF-α, and PGE(2), and therefore affect the anti-inflammatory effects.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antioxidant, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory activities of the ethanolic extracts of Taxillus liquidambaricola.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Oct 11;137(3):1161-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.07.041. Epub 2011 Jul 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21810460
-
Analgesic effects and mechanisms of anti-inflammation of taraxeren-3-one from Diospyros maritima in mice.J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Sep 14;59(17):9112-9. doi: 10.1021/jf201375u. Epub 2011 Aug 5. J Agric Food Chem. 2011. PMID: 21732622
-
Analgesic effects and the mechanisms of anti-inflammation of ergostatrien-3beta-ol from Antrodia camphorata submerged whole broth in mice.J Agric Food Chem. 2010 Jun 23;58(12):7445-52. doi: 10.1021/jf1013764. J Agric Food Chem. 2010. PMID: 20507140
-
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of a water extract of Trachelospermum jasminoides (Apocynaceae).J Ethnopharmacol. 2009 Nov 12;126(2):332-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.08.019. Epub 2009 Aug 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19703536
-
Anti-inflammatory activities of 6β-acetoxy-7α-hydroxyroyleanone from Taiwania cryptomerioides Hayata ex vivo and in vivo.J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Oct 26;59(20):11211-8. doi: 10.1021/jf200576f. Epub 2011 Sep 27. J Agric Food Chem. 2011. PMID: 21830830
Cited by
-
The genus Porana (Convolvulaceae) - A phytochemical and pharmacological review.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 18;13:998965. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.998965. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36330088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Scopoletin's Therapeutic Efficacy in DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis: Insights into Inflammatory Pathways, Immune Modulation, and Microbial Dynamics.Inflammation. 2025 Apr;48(2):575-589. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02048-9. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 38918333 Free PMC article.
-
Coumarin: A natural solution for alleviating inflammatory disorders.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2024 Sep 25;7:100202. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2024.100202. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 39398983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dried-leaf Artemisia annua: A practical malaria therapeutic for developing countries?World J Pharmacol. 2014 Dec 9;3(4):39-55. doi: 10.5497/wjp.v3.i4.39. World J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25678989 Free PMC article.
-
Angelica dahurica Extracts Attenuate CFA-Induced Inflammatory Pain via TRPV1 in Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 May 23;2022:4684830. doi: 10.1155/2022/4684830. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35656472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Noh JR, Kim YH, Gang GT, et al. Hepatoprotective effects of chestnut (Castanea crenata) inner shell extract against chronic ethanol-induced oxidative stress in C57BL/6 mice. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2011;49(7):1537–1543. - PubMed
-
- Chang TN, Ho YL, Huang GJ, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of Crossostephium chinensis (L.) makino in rats. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine. 2011;39(3):503–521. - PubMed
-
- Noh JR, Gang GT, Kim YH, et al. Antioxidant effects of the chestnut (Castanea crenata) inner shell extract in t-BHP-treated HepG2 cells, and CCl4- and high-fat diet-treated mice. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2010;48(11):3177–3183. - PubMed
-
- Kim HJ, Jang SI, Kim YJ, et al. Scopoletin suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokines and PGE2 from LPS-stimulated cell line, RAW 264.7 cells. Fitoterapia. 2004;75(3-4):261–266. - PubMed
-
- Kidd BL, Photiou A, Inglis JJ. The role of inflammatory mediators on nociception and pain in arthritis. Novartis Foundation Symposium. 2004;260:122–133. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

