Temporomandibular Disorders and Related Factors in a Group of Iranian Adolescents: A Cross-sectional Survey
- PMID: 22991620
- PMCID: PMC3442434
- DOI: 10.5681/joddd.2011.028
Temporomandibular Disorders and Related Factors in a Group of Iranian Adolescents: A Cross-sectional Survey
Abstract
Background and aims: Temporomandibular disorders (TMDs) are the most common condition affecting the tem-poromandibular joint and associated structures. The aim of this study was the epidemiologic evaluation of TMDs and re-lated factors in a group of Iranian adolescents.
Materials and methods: This descriptive cross-sectional survey included a sample of800 high school students (400 girls and 400 boys) aged 14 to18 years, in Mashhad, Iran, selected using cluster sampling. Examiners completed question-naires and performed the clinical examinations. Data were analyzed with the Chi-square and Fisher exact tests.
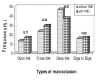
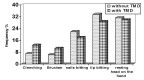
Results: The prevalence of TMDs in the studied sample was 34.7%. The most common signs of TMDs were clicking, muscle tenderness and TMJ tenderness. The most prevalent predisposing factors of TMDs were clenching, premature con-tact in protrusive movement and bruxism. A clear predominance was seen in girls (40.5%) compared with boys (29%) (P = 0.001).
Conclusion: Signs and symptoms of TMDs were prevalent in Iranian adolescents with a clear female predominance.
Keywords: Adolescent; epidemiology; temporomandibular joint disorders.
References
-
- de oliveira as, dias em, contato rg, berzin f. prevalence study of signs and symptoms of temporomandibular disorder in brazilian college students. braz oral res. 2006;20:3–7. - PubMed
-
- otuyemi od, owotade fj, ugboko vi, ndukwe kc, olusile oa. prevalence of signs and symptoms of temporomandibular disorders in young nigerian adults. j orthod. 2000;27:61–5. - PubMed
-
- rollman gb, gillespie jm. the role of psychosocial factors in temporomandibular disorders. curr rev pain. 2000;4:71–81. - PubMed
-
- okeson jp. management of temporomandibular disorders and occlusion. 6th ed. st. louis: mosby; 2008. 140-9, 164-5
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources