Lipoprotein(a): Cellular Effects and Molecular Mechanisms
- PMID: 22991657
- PMCID: PMC3443569
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/923289
Lipoprotein(a): Cellular Effects and Molecular Mechanisms
Abstract
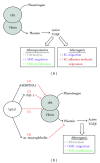
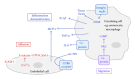
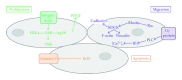
Lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)) is an independent risk factor for the development of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Indeed, individuals with plasma concentrations >20 mg/dL carry a 2-fold increased risk of developing CVD, accounting for ~25% of the population. Circulating levels of Lp(a) are remarkably resistant to common lipid lowering therapies, and there are currently no robust treatments available for reduction of Lp(a) apart from plasma apheresis, which is costly and labour intensive. The Lp(a) molecule is composed of two parts, an LDL/apoB-100 core and a unique glycoprotein, apolipoprotein(a) (apo(a)), both of which can interact with components of the coagulation cascade, inflammatory pathways, and cells of the blood vessel wall (smooth muscle cells (SMC) and endothelial cells (EC)). Therefore, it is of key importance to determine the molecular pathways by which Lp(a) exerts its influence on the vascular system in order to design therapeutics to target its cellular effects. This paper will summarise the role of Lp(a) in modulating cell behaviour in all aspects of the vascular system including platelets, monocytes, SMC, and EC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lipoprotein(a) - Link between Atherogenesis and Thrombosis.Prague Med Rep. 2019;120(2-3):39-51. doi: 10.14712/23362936.2019.9. Prague Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31586503 Review.
-
Apolipoprotein(a) acts as a chemorepellent to human vascular smooth muscle cells via integrin αVβ3 and RhoA/ROCK-mediated mechanisms.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;45(8):1776-83. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.05.021. Epub 2013 May 31. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23726972 Free PMC article.
-
Potent lipoprotein(a) lowering following apolipoprotein(a) antisense treatment reduces the pro-inflammatory activation of circulating monocytes in patients with elevated lipoprotein(a).Eur Heart J. 2020 Jun 21;41(24):2262-2271. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa171. Eur Heart J. 2020. PMID: 32268367 Free PMC article.
-
Low-density lipoprotein apheresis: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2007;7(5):1-101. Epub 2006 Nov 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2007. PMID: 23074505 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoprotein(a), cardiovascular disease, and contemporary management.Mayo Clin Proc. 2013 Nov;88(11):1294-311. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.09.003. Mayo Clin Proc. 2013. PMID: 24182706 Review.
Cited by
-
Pleiotropic Effects of PCSK9: Focus on Thrombosis and Haemostasis.Metabolites. 2022 Mar 4;12(3):226. doi: 10.3390/metabo12030226. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35323669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenetic gene changes of eutopic endometrium in patients with ovarian endometriosis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2019 May 5;132(9):1107-1109. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000195. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019. PMID: 30882467 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Variations of lipoprotein(a) levels in the metabolic syndrome: a report from the Maracaibo City Metabolic Syndrome Prevalence Study.J Diabetes Res. 2013;2013:416451. doi: 10.1155/2013/416451. Epub 2013 Apr 22. J Diabetes Res. 2013. PMID: 23710466 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoprotein(a) the Insurgent: A New Insight into the Structure, Function, Metabolism, Pathogenicity, and Medications Affecting Lipoprotein(a) Molecule.J Lipids. 2020 Feb 1;2020:3491764. doi: 10.1155/2020/3491764. eCollection 2020. J Lipids. 2020. PMID: 32099678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between lipoprotein(a) concentration and the risk of stroke in the Chinese Han population: a retrospective case-control study.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Mar;8(5):212. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.01.38. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32309359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marcovina SM, Koschinsky ML, Albers JJ, Skarlatos S. Report of the national heart, lung, and blood institute workshop on Lipoprotein(a) and cardiovascular disease: recent advances and future directions. Clinical Chemistry. 2003;49(11):1785–1796. - PubMed
-
- Frank S, Durovic S, Kostner GM. The assembly of lipoprotein Lp(a) European Journal of Clinical Investigation. 1996;26(2):109–114. - PubMed
-
- Berg K. A new serum type system in man—the Lp system. Acta Pathologica et Microbiologica Scandinavica. 1963;59:369–382. - PubMed
-
- Kostner GM, Avogaro P, Cazzolato G. Lipoprotein Lp(a) and the risk for myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis. 1981;38(1-2):51–61. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

