Optimization of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry analysis for bacterial identification
- PMID: 22993178
- PMCID: PMC3502975
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00626-12
Optimization of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry analysis for bacterial identification
Abstract
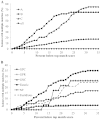
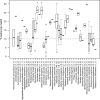
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) is a relatively new addition to the clinical microbiology laboratory. The performance of the MALDI Biotyper system (Bruker Daltonics) was compared to those of phenotypic and genotypic identification methods for 690 routine and referred clinical isolates representing 102 genera and 225 unique species. We systematically compared direct-smear and extraction methods on a taxonomically diverse collection of isolates. The optimal score thresholds for bacterial identification were determined, and an approach to address multiple divergent results above these thresholds was evaluated. Analysis of identification scores revealed optimal species- and genus-level identification thresholds of 1.9 and 1.7, with 91.9% and 97.0% of isolates correctly identified to species and genus levels, respectively. Not surprisingly, routinely encountered isolates showed higher concordance than did uncommon isolates. The extraction method yielded higher scores than the direct-smear method for 78.3% of isolates. Incorrect species were reported in the top 10 results for 19.4% of isolates, and although there was no obvious cutoff to eliminate all of these ambiguities, a 10% score differential between the top match and additional species may be useful to limit the need for additional testing to reach single-species-level identifications.
Figures

References
-
- Alatoom AA, Cunningham SA, Ihde SM, Mandrekar J, Patel R. 2011. Comparison of direct colony method versus extraction method for identification of Gram-positive cocci by use of Bruker Biotyper matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 49:2868–2873 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

