Intestine-specific expression of Apobec-1 rescues apolipoprotein B RNA editing and alters chylomicron production in Apobec1 -/- mice
- PMID: 22993231
- PMCID: PMC3494256
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M030494
Intestine-specific expression of Apobec-1 rescues apolipoprotein B RNA editing and alters chylomicron production in Apobec1 -/- mice
Abstract
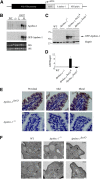
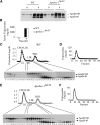
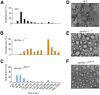
Intestinal apolipoprotein B (apoB) mRNA undergoes C-to-U editing, mediated by the catalytic deaminase apobec-1, which results in translation of apoB48. Apobec1(-/-) mice produce only apoB100 and secrete larger chylomicron particles than those observed in wild-type (WT) mice. Here we show that transgenic rescue of intestinal apobec-1 expression (Apobec1(Int/O)) restores C-to-U RNA editing of apoB mRNA in vivo, including the canonical site at position 6666 and also at approximately 20 other newly identified downstream sites present in WT mice. The small intestine of Apobec1(Int/O) mice produces only apoB48, and the liver produces only apoB100. Serum chylomicron particles were smaller in Apobec1(Int/O) mice compared with those from Apobec1(-/-) mice, and the predominant fraction of serum apoB48 in Apobec1(Int/O) mice migrated in lipoproteins smaller than chylomicrons, even when these mice were fed a high-fat diet. Because apoB48 arises exclusively from the intestine in Apobec1(Int/O) mice and intestinal apoB48 synthesis and secretion rates were comparable to WT mice, we were able to infer the major sites of origin of serum apoB48 in WT mice. Our findings imply that less than 25% of serum apoB48 in WT mice arises from the intestine, with the majority originating from the liver.
Figures






References
-
- Chen Z., Davidson N.O.2006. Genetic regulation of intestinal lipid transport and metabolism. In Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. L. R. Johnson, editor. Elsevier Academic Press, Boston, MA. 1711–1734.
-
- Teng B., Burant C. F., Davidson N. O. 1993. Molecular cloning of an apolipoprotein B messenger RNA editing protein. Science. 260: 1816–1819 - PubMed
-
- Lellek H., Kirsten R., Diehl I., Apostel F., Buck F., Greeve J. 2000. Purification and molecular cloning of a novel essential component of the apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme-complex. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 19848–19856 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

