Titrating Optimal Dose of Osmotic-Controlled Release Oral Delivery (OROS)-Methylphenidate and Its Efficacy and Safety in Korean Children with ADHD: A Multisite Open Labeled Study
- PMID: 22993525
- PMCID: PMC3440475
- DOI: 10.4306/pi.2012.9.3.257
Titrating Optimal Dose of Osmotic-Controlled Release Oral Delivery (OROS)-Methylphenidate and Its Efficacy and Safety in Korean Children with ADHD: A Multisite Open Labeled Study
Abstract
Objective: This study was aimed to determine effectiveness and tolerability of Osmotic-controlled Release Oral delivery (OROS) methylphenidate (MPH) and its optimal dose administered openly over a period of up to 12 weeks in drug naïve Korean children with ADHD.
Methods: Subjects (n=143), ages 6 to 18-years, with a clinical diagnosis of any subtype of ADHD were recruited from 7 medical centers in Korea. An individualized dose of OROS-MPH was determined for each subject depending on the response criteria. The subjects were assessed with several symptom rating scales in week 1, 3, 6, 9 and 12.
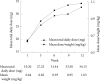
Results: 77 of 116 subjects (66.4%) achieved the criteria for response and the average of optimal daily dose for response was to 30.05±12.52 mg per day (0.90±0.31 mg/kg/d) at the end of the study. Optimal dose was not significantly different between ADHD subtypes, whereas, significant higher dose was needed in older aged groups than younger groups. The average of optimal daily dose for response for the subjects aged above 12 years old was 46.38±15.52 per day (0.81±0.28 mg/kg/d) compared to younger groups (p<0.01). No serious adverse effects were reported and the dose did not have a significant effect on adverse effects.
Conclusion: Optimal mean dose of OROS-MPH was significantly different by age groups. Higher dose was needed in older aged groups than younger groups. Effectiveness and tolerability of OROS-MPH in symptoms of ADHD is sustained for up to 12 weeks.
Keywords: ADHD; OROS-MPH; Optimal dose.
Figures
References
-
- Wilens TE, Bierderman J, Spencer TJ. Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder across the lifespan. Ann Rev Med. 2002;53:113–131. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- Barkley R, Fischer M, Edelbrock CS, Smallish L. The adolescent outcome of hyperactive children diagnosed by research criteria: I. An 8-year prospective follow-up study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1990;29:546–557. - PubMed
-
- Mannuzza S, Klein RG, Bessler A, Malloy P, LaPadula M. Adult outcome of hyperactive boys. Educational achievement, occupational rank, and psychiatric status. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993;50:565–576. - PubMed
-
- Lilienfeld S, Waldman ID. The relation between childhood attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and adult antisocial behavior reexamined: the problem of heterogeneoity. Clin Psychol Rev. 1990;10:699–725.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources