Neurogenic mucosal bicarbonate secretion in guinea pig duodenum
- PMID: 22994306
- PMCID: PMC3631377
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02218.x
Neurogenic mucosal bicarbonate secretion in guinea pig duodenum
Abstract
Background and purpose: To test a hypothesis that: (i) duodenal pH and osmolarity are individually controlled at constant set points by negative feedback control centred in the enteric nervous system (ENS); (ii) the purinergic P2Y(1) receptor subtype is expressed by non-cholinergic secretomotor/vasodilator neurons, which represent the final common excitatory pathway from the ENS to the bicarbonate secretory glands.
Experimental approach: Ussing chamber and pH-stat methods investigated involvement of the P2Y(1) receptor in neurogenic stimulation of mucosal bicarbonate (HCO(3)(-)) secretion in guinea pig duodenum.
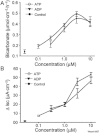
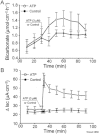
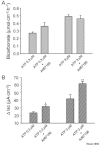
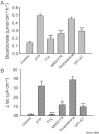
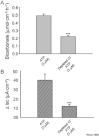
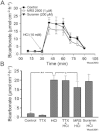
Key results: ATP increased HCO(3)(-) secretion with an EC(50) of 160 nM. MRS2179, a selective P2Y(1) purinergic receptor antagonist, suppressed ATP-evoked HCO(3)(-) secretion by 47% and Cl(-) secretion by 63%. Enteric neuronal blockade by tetrodotoxin or exposure to a selective vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP, VPAC(1)) receptor antagonist suppressed ATP-evoked HCO(3)(-) secretion by 61 and 41%, respectively, and Cl- by 97 and 70% respectively. Pretreatment with the muscarinic antagonist, scopolamine did not alter ATP-evoked HCO3(-) or Cl(-) secretion.
Conclusion and implications: Whereas acid directly stimulates the mucosa to release ATP and stimulate HCO(3)(-) secretion in a cytoprotective manner, neurogenically evoked HCO(3)(-) secretion accounts for feedback control of optimal luminal pH for digestion. ATP stimulates duodenal HCO(3)(-) secretion through an excitatory action at purinergic P2Y(1) receptors on neurons in the submucosal division of the ENS. Stimulation of the VIPergic non-cholinergic secretomotor/vasodilator neurons, which are one of three classes of secretomotor neurons, accounts for most, if not all, of the neurogenic secretory response evoked by ATP.
© 2012 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2012 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Bornstein JC, Furness JB. Correlated electrophysiological and histochemical studies of submucous neurons and their contribution to understanding enteric neural circuits. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1988;25:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Bornstein JC, Gwynne RM, Sjovall H. Enteric neural regulation of mucosal secretion. In: Johnson LR, Ghishan FK, Kaunitz JD, Merchant JL, Said HM, Wood JD, editors. Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Track. San Diego, CA: Elsevier Academic Press; 2012. pp. 769–790.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

