Fasudil ameliorates disease progression in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, acting possibly through antiinflammatory effect
- PMID: 22994384
- PMCID: PMC6493591
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12002
Fasudil ameliorates disease progression in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, acting possibly through antiinflammatory effect
Abstract
Aim: The purpose of this investigation was to further explore the mechanism(s) underlying the amelioration in EAE caused by Fasudil, particularly focusing on anti-inflammatory effect.
Methods: We induced a chronic-progressive experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in B6 mice immunized with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein(35-55) and performed Fasudil intervention in early and late stages of the disease.
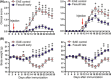
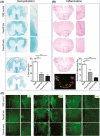
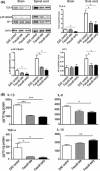
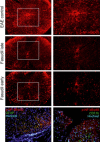
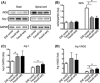
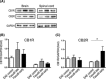
Results: The administration of Fasudil (40 mg/kg, i.p) had a therapeutic effect in delaying the onset and ameliorating the severity of EAE, accompanied by the improvement in myelination and the decrease in inflammatory cells in spinal cords. Fasudil inhibited TLR-4, p-NF-kB/p65, and inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) and enhanced IL-10 production in spinal cords. The ratio of arginase/iNOS was enhanced mainly in the spinal cords of EAE mice treated with Fasudil, reflecting a shift toward the M2 (antiinflammation) macrophage/microglia phenotype. The administration of Fasudil also induced the upregulation of CB2 receptor in spinal cords, but did not significantly trigger CB1 receptor. Levels of neurotrophic factors NGF, BDNF, and GDNF in the CNS were not altered by Fasudil.
Conclusion: Fasudil ameliorates disease progression in EAE, acting possibly through antiinflammatory pathway.
© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tselis A. Evidence for viral etiology of multiple sclerosis. Semin Neurol 2011;31:307–316. - PubMed
-
- Stadelmann C, Wegner C, Brück W. Inflammation, demyelination, and degeneration – recent insights from MS pathology. Biochim Biophys Acta 2011;1812:275–282. - PubMed
-
- Tuohy VK, Yu M, Yin L, et al. The epitope spreading cascade during progression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis. Immunol Rev 1998;164:93–100. - PubMed
-
- Sospedra M, Martin R. Immunology of multiple sclerosis. Annu Rev Immunol 2005;23:683–747. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

