The unique paradigm of spirochete motility and chemotaxis
- PMID: 22994496
- PMCID: PMC3771095
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-micro-092611-150145
The unique paradigm of spirochete motility and chemotaxis
Abstract
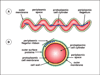
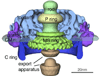
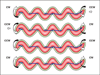
Spirochete motility is enigmatic: It differs from the motility of most other bacteria in that the entire bacterium is involved in translocation in the absence of external appendages. Using the Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi (Bb) as a model system, we explore the current research on spirochete motility and chemotaxis. Bb has periplasmic flagella (PFs) subterminally attached to each end of the protoplasmic cell cylinder, and surrounding the cell is an outer membrane. These internal helix-shaped PFs allow the spirochete to swim by generating backward-moving waves by rotation. Exciting advances using cryoelectron tomography are presented with respect to in situ analysis of cell, PF, and motor structure. In addition, advances in the dynamics of motility, chemotaxis, gene regulation, and the role of motility and chemotaxis in the life cycle of Bb are summarized. The results indicate that the motility paradigms of flagellated bacteria do not apply to these unique bacteria.
Figures

References
Literature Cited
-
- Akerley BJ, Cotter PA, Miller JF. Ectopic expression of the flagellar regulon alters development of the Bordetella-host interaction. Cell. 1995;80:611–620. - PubMed
-
- Babitzke P, Romeo T. CsrB sRNA family: sequestration of RNA-binding regulatory proteins. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2007;10:156–163. - PubMed
Related Resources
-
- Samuels DS. Gene regulation in Borrelia burgdorferi. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2011;65:479–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

