HIV-1 subtype C superinfected individuals mount low autologous neutralizing antibody responses prior to intrasubtype superinfection
- PMID: 22995123
- PMCID: PMC3477039
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4690-9-76
HIV-1 subtype C superinfected individuals mount low autologous neutralizing antibody responses prior to intrasubtype superinfection
Abstract
Background: The potential role of antibodies in protection against intra-subtype HIV-1 superinfection remains to be understood. We compared the early neutralizing antibody (NAb) responses in three individuals, who were superinfected within one year of primary infection, to ten matched non-superinfected controls from a Zambian cohort of subtype C transmission cases. Sequence analysis of single genome amplified full-length envs from a previous study showed limited diversification in the individuals who became superinfected with the same HIV-1 subtype within year one post-seroconversion. We hypothesized that this reflected a blunted NAb response, which may have made these individuals more susceptible to superinfection.
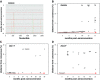
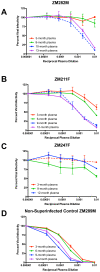
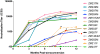
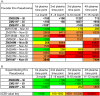
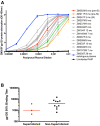
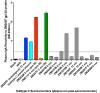
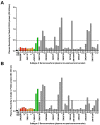
Results: Neutralization assays showed that autologous plasma NAb responses to the earliest, and in some cases transmitted/founder, virus were delayed and had low to undetectable titers in all three superinfected individuals prior to superinfection. In contrast, NAbs with a median IC50 titer of 1896 were detected as early as three months post-seroconversion in non-superinfected controls. Early plasma NAbs in all subjects showed limited but variable levels of heterologous neutralization breadth. Superinfected individuals also exhibited a trend toward lower levels of gp120- and V1V2-specific IgG binding antibodies but higher gp120-specific plasma IgA binding antibodies.
Conclusions: These data suggest that the lack of development of IgG antibodies, as reflected in autologous NAbs as well as gp120 and V1V2 binding antibodies to the primary infection virus, combined with potentially competing, non-protective IgA antibodies, may increase susceptibility to superinfection in the context of settings where a single HIV-1 subtype predominates.
Figures

References
-
- Hessell AJ, Rakasz EG, Poignard P, Hangartner L, Landucci G, Forthal DN, Koff WC, Watkins DI, Burton DR. Broadly neutralizing human anti-HIV antibody 2G12 is effective in protection against mucosal SHIV challenge even at low serum neutralizing titers. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5:e1000433. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000433. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mascola JR, Stiegler G, VanCott TC, Katinger H, Carpenter CB, Hanson CE, Beary H, Hayes D, Frankel SS, Birx DL, Lewis MG. Protection of macaques against vaginal transmission of a pathogenic HIV-1/SIV chimeric virus by passive infusion of neutralizing antibodies. Nat Med. 2000;6:207–210. doi: 10.1038/72318. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- KL2 TR000455/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 2D43 TW001042/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI-51235/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI-007470/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI-78410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI051231/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI046283/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI-58706/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI091514-01A1/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR-025009/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P51RR165/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050409/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI051231/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P51OD11132/OD/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

