Antitubercular nitrofuran isoxazolines with improved pharmacokinetic properties
- PMID: 22995771
- PMCID: PMC3582038
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.08.023
Antitubercular nitrofuran isoxazolines with improved pharmacokinetic properties
Abstract
A series of tetracyclic nitrofuran isoxazoline anti-tuberculosis agents was designed and synthesized to improve the pharmacokinetic properties of an initial lead compound, which had potent anti-tuberculosis activity but suffered from poor solubility, high protein binding and rapid metabolism. In this study, structural modifications were carried on the outer phenyl and piperidine rings to introduce solubilizing and metabolically blocking functional groups. The compounds generated were evaluated for their in vitro antitubercular activity, bacterial spectrum of activity, solubility, permeability, microsomal stability and protein binding. Pharmacokinetic profiles for the most promising candidates were then determined. Compounds with phenyl morpholine and pyridyl morpholine outer rings were found to be the most potent anti-tuberculosis agents in the series. These compounds retained a narrow antibacterial spectrum of activity, with weak anti-Gram positive and no Gram negative activity, as well as good activity against non-replicating Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a low oxygen model. Overall, the addition of solubilizing and metabolically blocked outer rings did improve solubility and decrease protein binding as designed. However, the metabolic stability for compounds in this series was generally lower than desired. The best three compounds selected for in vivo pharmacokinetic testing all showed high oral bioavailability, with one notable compound showing a significantly longer half-life and good tolerability supporting its further advancement.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

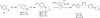
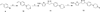
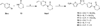
Similar articles
-
Pentacyclic nitrofurans with in vivo efficacy and activity against nonreplicating Mycobacterium tuberculosis.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 5;9(2):e87909. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087909. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24505329 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of novel isoxazolines as anti-tuberculosis agents.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Dec 1;17(23):6638-42. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.09.048. Epub 2007 Sep 15. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007. PMID: 17937983 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of N-benzyl-5-nitrofuran-2-carboxamide as an antitubercular agent.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019 Feb 15;29(4):601-606. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.12.053. Epub 2018 Dec 24. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019. PMID: 30600207 Free PMC article.
-
Current development of 5-nitrofuran-2-yl derivatives as antitubercular agents.Bioorg Chem. 2019 Jul;88:102969. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.102969. Epub 2019 May 2. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31077910 Review.
-
Nitrofurans as novel anti-tuberculosis agents: identification, development and evaluation.Curr Top Med Chem. 2007;7(5):509-26. doi: 10.2174/156802607780059772. Curr Top Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17346196 Review.
Cited by
-
Nitrile Oxide, Alkenes, Dipolar Cycloaddition, Isomerization and Metathesis Involved in the Syntheses of 2-Isoxazolines.Molecules. 2023 Mar 10;28(6):2547. doi: 10.3390/molecules28062547. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36985520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pentacyclic nitrofurans that rapidly kill nifurtimox-resistant trypanosomes.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016 Apr;71(4):956-63. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkv417. Epub 2015 Dec 18. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016. PMID: 26682963 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Activity Relationships of Spectinamide Antituberculosis Agents: A Dissection of Ribosomal Inhibition and Native Efflux Avoidance Contributions.ACS Infect Dis. 2017 Jan 13;3(1):72-88. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.6b00158. Epub 2016 Nov 11. ACS Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28081607 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and antibacterial evaluation of macrocyclic diarylheptanoid derivatives.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016 Aug 15;26(16):4070-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.06.075. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016. PMID: 27406794 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical modulation of the biological activity of reutericyclin: a membrane-active antibiotic from Lactobacillus reuteri.Sci Rep. 2014 Apr 17;4:4721. doi: 10.1038/srep04721. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24739957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailer AJ. Testing for the equality of area under the curves when using destructive measurement techniques. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1988;16:303–309. - PubMed
-
- Yee D, Valiquette C, Pelletier M, Parisien I, Rocher I, Menzies D. Incidence of serious side effects from first-line antituberculosis drugs among patients treated for active tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;167:1472–1477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

