The utility of uterine artery Doppler velocimetry in prediction of preeclampsia in a low-risk population
- PMID: 22996099
- PMCID: PMC3449210
- DOI: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e31826af7fb
The utility of uterine artery Doppler velocimetry in prediction of preeclampsia in a low-risk population
Abstract
Objective: The underlying pathophysiology of preeclampsia is thought to be abnormal trophoblast invasion of the spiral arteries leading to maldevelopment of uteroplacental perfusion. We estimated whether uterine artery Doppler measurements made in the early second trimester would predict the subsequent development of preeclampsia.
Methods: Uterine artery Doppler measurements before 21 weeks of gestation (median 16.6 weeks) were correlated with subsequent development of preeclampsia in a cohort of 2,188 low-risk nulliparous women in a randomized control trial of antioxidant supplementation for prevention of preeclampsia. Preeclampsia developed in 165 (7.5%) women.
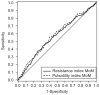
Results: Development of preeclampsia overall was associated with increased resistance index, pulsatility index, a pulsatility index or resistance index multiple of the median at or above the 75th percentile but not the presence of a notch or a bilateral notch before 21 weeks of gestation. The sensitivity was 43% (95% confidence interval [CI] 35-51) and specificity 67% (95% CI 65-69) for prediction of preeclampsia overall. The presence of a notch or bilateral notch, resistance index, and pulsatility index multiple of the median was significantly associated with early onset (before 34 weeks of gestation) compared with late onset or no preeclampsia (odds ratio [OR] 6.9, 95% CI 2.3-20.9; sensitivity 78%, 95% CI 52-94; specificity 66%, 95% CI 64-68). The presence of a notch or resistance index multiple of the median at or above the 75th percentile increased the odds of developing severe compared with mild or no preeclampsia (OR 2.2, 95% CI 1.4-3.7; sensitivity 53%, 95% CI 40-65; specificity 66%, 95% CI 64-68).
Conclusion: Our data show poor sensitivity of second-trimester Doppler ultrasound measurements for prediction of preeclampsia overall in a well-characterized, low-risk, nulliparous population. The technique has utility in identifying poor trophoblast invasion of spiral arteries of a magnitude that severely compromises uteroplacental blood flow and gives early-onset disease.
Level of evidence: II.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Estimates of maternal mortality: a new approach by WHO and UNICED. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1996.
-
- Which anticonvulsant for women with eclampsia? Evidence from the Collaborative Eclampsia Trial. Lancet. 1995;345:1455–63. - PubMed
-
- McDonald SD, Malinowski A, Zhou Q, Yusuf S, Devereaux PJ. Cardiovascular sequelae of preeclampsia/eclampsia: a systematic review and meta-analyses. Am Heart J. 2008 Nov;156(5):918–30. - PubMed
-
- Papageorghiou AT, Yu CK, Nicolaides KH. The role of uterine artery Doppler in predicting adverse pregnancy outcome. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2004 Jun;18(3):383–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HD36801/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040500/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027869/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034136/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040485/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40485/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40560/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040560/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040512/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD036801/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053118/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000150/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040544/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD034116/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27869/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD34136/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040560/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD53118/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD053097/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27860/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027915/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40512/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040544/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD034208/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR00080/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040512/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40545/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034116/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD21410/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027869/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027917/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD34116/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027915/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040545/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040485/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027860/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40500/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034208/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053097/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD34208/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27915/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040500/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27917/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021410/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000080/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HD036801/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD036801/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD53097/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040545/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40544/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

