Salvianolic acid A protects the peripheral nerve function in diabetic rats through regulation of the AMPK-PGC1α-Sirt3 axis
- PMID: 22996345
- PMCID: PMC6268602
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules170911216
Salvianolic acid A protects the peripheral nerve function in diabetic rats through regulation of the AMPK-PGC1α-Sirt3 axis
Abstract
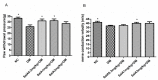
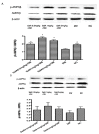
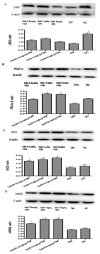
Salvianolic acid A (SalA) is one of the main efficacious, water-soluble constituents of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. This study investigated the protective effects of SalA on peripheral nerve in diabetic rats. Administration of SalA (0.3, 1 and 3 mg/kg, ig) was started from the 5th week after strepotozotocin (STZ60 mg/kg) intraperitoneal injection and continued for 8 weeks. Paw withdrawal mechanical threshold (PWMT) and motor nerve conduction velocity (MNCV) were used to assess peripheral nerve function. The western blot methods were employed to test the expression levels of serine-threonine liver kinase B1 (LKB1), AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1alpha (PGC-1α), silent information regulator protein3 (sirtuin 3/Sirt3) and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) in sciatic nerve. Results showed that SalA administration could increase PWMT and MNCV in diabetic rats; reduce the deterioration of sciatic nerve pathology; increase AMPK phosphorylation level, up-regulate PGC-1α, Sirt3 and nNOS expression, but had no influence on LKB1. These results suggest that SalA has protective effects against diabetic neuropathy. The beneficial effects of SalA on peripheral nerve function in diabetic rats might be attributed to improvements in glucose metabolism through regulation of the AMPK-PGC1α-Sirt3 axis.
Figures


References
-
- Tesfaye S., Boulton A.J., Dyck P.J., Freeman R., Horowitz M., Kempler P., Lauria G., Malik R.A., Spallone V., Vinik A., et al. Diabetic neuropathies: Update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes Care. 2010;33:2285–2293. doi: 10.2337/dc10-1303. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

