An anatomically comprehensive atlas of the adult human brain transcriptome
- PMID: 22996553
- PMCID: PMC4243026
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11405
An anatomically comprehensive atlas of the adult human brain transcriptome
Abstract
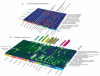
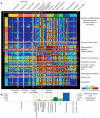
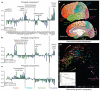
Neuroanatomically precise, genome-wide maps of transcript distributions are critical resources to complement genomic sequence data and to correlate functional and genetic brain architecture. Here we describe the generation and analysis of a transcriptional atlas of the adult human brain, comprising extensive histological analysis and comprehensive microarray profiling of ∼900 neuroanatomically precise subdivisions in two individuals. Transcriptional regulation varies enormously by anatomical location, with different regions and their constituent cell types displaying robust molecular signatures that are highly conserved between individuals. Analysis of differential gene expression and gene co-expression relationships demonstrates that brain-wide variation strongly reflects the distributions of major cell classes such as neurons, oligodendrocytes, astrocytes and microglia. Local neighbourhood relationships between fine anatomical subdivisions are associated with discrete neuronal subtypes and genes involved with synaptic transmission. The neocortex displays a relatively homogeneous transcriptional pattern, but with distinct features associated selectively with primary sensorimotor cortices and with enriched frontal lobe expression. Notably, the spatial topography of the neocortex is strongly reflected in its molecular topography-the closer two cortical regions, the more similar their transcriptomes. This freely accessible online data resource forms a high-resolution transcriptional baseline for neurogenetic studies of normal and abnormal human brain function.
Figures



Comment in
-
Neurogenetics: mapping gene expression in the human brain.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012 Nov;13(11):737. doi: 10.1038/nrn3370. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23072913 No abstract available.
-
The genetic essence of our brains.Nat Methods. 2012 Nov;9(11):1044-5. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2236. Nat Methods. 2012. PMID: 23281566 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

