Interleukin-1α is the major alarmin of lung epithelial cells released during photodynamic therapy to induce inflammatory mediators in fibroblasts
- PMID: 22996613
- PMCID: PMC3493767
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2012.429
Interleukin-1α is the major alarmin of lung epithelial cells released during photodynamic therapy to induce inflammatory mediators in fibroblasts
Abstract
Background: Photodynamic therapy (PDT) causes tissue damage that initiates a local inflammatory response. Post-PDT reactions are considered to assist in mobilising the immune system thereby affecting tumour recurrence. The initiating process of the PDT-dependent tissue reaction remains to be determined.
Methods: Primary cultures of human lung cells were established. The photoreaction mediated by pyropheophorbide-a, at specific subcellular sites and levels resulting in the release of alarmins by epithelial cells (Eps), was defined by immunoblot analyses and expression profiling. The activity of Ep-derived factors to stimulate expression of proinflammatory mediators, including IL-6, and to enhance neutrophil binding by fibroblasts (Fbs) was determined by functional bioassays.
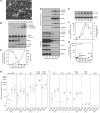
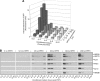
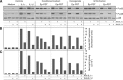
Results: Epithelial cells release IL-1β as the primary Fb-stimulatory activity under basal conditions. Intracellular IL-1α, externalised following photoreaction, accounts for most of the PDT-mediated Fb activation. Expression of IL-1 is subject to increase or loss during oncogenic transformation resulting in altered alarmin functions mobilisable by PDT. Photoreaction by a cell surface-bound photosensitiser (PS) is 10-fold more effective than PSs localised to mitochondria or lysosomes. High-dose intracellular, but not cell surface, photoreaction inactivates IL-1 and reduces Fb stimulation.
Conclusion: These in vitro data suggest that the subcellular site and intensity of photoreaction influence the magnitude of the stromal cell response to the local damage and, in part, support the relationship of PDT dose and level of post-PDT inflammatory response observed in vivo.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal interaction during photodynamic therapy-induced photorejuvenation.Arch Dermatol Res. 2016 Sep;308(7):493-501. doi: 10.1007/s00403-016-1666-3. Epub 2016 Jul 6. Arch Dermatol Res. 2016. PMID: 27383261
-
IL-1α released from damaged epithelial cells is sufficient and essential to trigger inflammatory responses in human lung fibroblasts.Mucosal Immunol. 2014 May;7(3):684-93. doi: 10.1038/mi.2013.87. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Mucosal Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24172847 Free PMC article.
-
The alarmin IL-1α is a master cytokine in acute lung inflammation induced by silica micro- and nanoparticles.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2014 Dec 13;11:69. doi: 10.1186/s12989-014-0069-x. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 25497724 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-1α drives the dysfunctional cross-talk of the airway epithelium and lung fibroblasts in COPD.Eur Respir J. 2016 Aug;48(2):359-69. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01911-2015. Epub 2016 Jul 13. Eur Respir J. 2016. PMID: 27418555
-
Mechanisms of lung fibrosis induced by carbon nanotubes: towards an Adverse Outcome Pathway (AOP).Part Fibre Toxicol. 2016 Feb 29;13:11. doi: 10.1186/s12989-016-0123-y. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26926090 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Time Rules the Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Photodynamic Therapy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Jul;9(21):e2200999. doi: 10.1002/advs.202200999. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 35470595 Free PMC article.
-
The immunobiology of preterm labor and birth: intra-amniotic inflammation or breakdown of maternal-fetal homeostasis.Reproduction. 2022 Jun 20;164(2):R11-R45. doi: 10.1530/REP-22-0046. Reproduction. 2022. PMID: 35559791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apremilast ameliorates IL-1α-induced dysfunction in epidermal stem cells.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Aug 10;13(15):19293-19305. doi: 10.18632/aging.203265. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34375302 Free PMC article.
-
The IL-1 cytokine family and its role in inflammation and fibrosis in the lung.Semin Immunopathol. 2016 Jul;38(4):517-34. doi: 10.1007/s00281-016-0559-z. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Semin Immunopathol. 2016. PMID: 27001429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic differences between phenotypes of chronic lung allograft dysfunction after lung transplantation.Transpl Int. 2014 Aug;27(8):857-67. doi: 10.1111/tri.12341. Epub 2014 Jun 17. Transpl Int. 2014. PMID: 24750386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baumann H, Gauldie J (1994) The acute phase response. Immunol Today 15(2): 74–80 - PubMed
-
- Baumann H, Prowse KR, Marinkovic S, Won KA, Jahreis GP (1989) Stimulation of hepatic acute phase response by cytokines and glucocorticoids. Ann N Y Acad Sci 557: 280–295; discussion 295–296 - PubMed
-
- Bianchi ME (2007) DAMPs, PAMPs and alarmins: all we need to know about danger. J Leukoc Biol 81(1): 1–5 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

