Different analgesic effects of adenosine between postoperative and neuropathic pain
- PMID: 22996813
- PMCID: PMC3553403
- DOI: 10.1007/s00776-012-0302-0
Different analgesic effects of adenosine between postoperative and neuropathic pain
Abstract
Background: Adenosine is an endogenous neuromodulator in both the peripheral and central nervous systems. Adenosine inhibits pain signals by hyperpolarizing neuronal membrane.
Methods: To clarify the effects of adenosine on pain signals, we tested intrathecal adenosine injection in two neuropathic pains (spinal cord compression and chronic constriction of sciatic nerve) and postoperative pain (plantar incision).
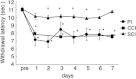
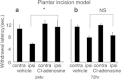
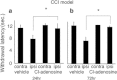
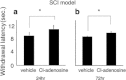
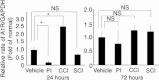
Results: In all three kinds of pain models, significant shortening of withdrawal latencies to thermal stimulation were detected from 24 h to 1 week after the surgery. Significant improvements of pain sensation were observed in all three models after intrathecal injection of Cl-adenosine 24 h after surgery. At 72 h after surgery, intrathecal Cl-adenosine injection inhibited hyperalgesia in the two neuropathic pain models but not in the postoperative pain model. Adenosine A1R messenger RNA (mRNA) expression significantly decreased in the plantar incision model. Adenosine A1R protein levels also decreased compared with the other two models and normal control.
Conclusions: These results suggest that adenosine effectively inhibits pain signals in neuropathic pain but is less effective in postoperative pain because of the decrease in adenosine A1 receptors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adenosine A1 but not A2a receptor agonist reduces hyperalgesia caused by a surgical incision in rats: a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein-dependent process.Anesthesiology. 2007 Nov;107(5):797-806. doi: 10.1097/01.anes.0000286982.36342.3f. Anesthesiology. 2007. PMID: 18073555
-
Phα1β, a peptide from the venom of the spider Phoneutria nigriventer shows antinociceptive effects after continuous infusion in a neuropathic pain model in rats.Anesth Analg. 2014 Jul;119(1):196-202. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000249. Anesth Analg. 2014. PMID: 24836473
-
Bidirectional Action of Cenicriviroc, a CCR2/CCR5 Antagonist, Results in Alleviation of Pain-Related Behaviors and Potentiation of Opioid Analgesia in Rats With Peripheral Neuropathy.Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 21;11:615327. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.615327. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33408720 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine for pain control.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand Suppl. 1997;110:135-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1997.tb05532.x. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand Suppl. 1997. PMID: 9248564 Review.
-
Clinical application of adenosine and ATP for pain control.J Anesth. 2005;19(3):225-35. doi: 10.1007/s00540-005-0310-8. J Anesth. 2005. PMID: 16032451 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Adenosine Receptors: A Potential Pharmacological Avenue for Acute and Chronic Pain.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 18;21(22):8710. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228710. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33218074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pilot prospective open-label one-arm trial investigating intrathecal Adenosine in neuropathic pain after lumbar discectomy.BMC Res Notes. 2020 Jun 12;13(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s13104-020-05133-y. BMC Res Notes. 2020. PMID: 32532345 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Adenosine signaling mediate pain transmission in the central nervous system.Purinergic Signal. 2023 Mar;19(1):245-254. doi: 10.1007/s11302-021-09826-2. Epub 2022 Jan 9. Purinergic Signal. 2023. PMID: 35000074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Underlying Mechanisms of Sleep Deprivation Exacerbating Neuropathic Pain.Nat Sci Sleep. 2023 Jul 28;15:579-591. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S414174. eCollection 2023. Nat Sci Sleep. 2023. PMID: 37533626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pain and Functional Scores in Patients Affected by Knee OA after Treatment with Pulsed Electromagnetic and Magnetic Fields: A Meta-Analysis.Cartilage. 2021 Dec;13(1_suppl):1749S-1760S. doi: 10.1177/1947603520931168. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Cartilage. 2021. PMID: 32508140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Obata H, Kimura M, Nakajima K, Tobe M, Nishikawa K, Saito S. Monoamine-dependent, opioid-independent antihypersensitivity effects of intrathecally administered milnacipran, a serotonin noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor, in a postoperative pain model in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010;334:1059–1065. doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.168336. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

