Exercise intensity self-regulation using the OMNI scale in children with cystic fibrosis
- PMID: 22997144
- PMCID: PMC3541455
- DOI: 10.1002/ppul.22639
Exercise intensity self-regulation using the OMNI scale in children with cystic fibrosis
Abstract
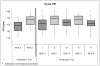
Prescribing exercise at intensities that improve fitness is difficult in children with cystic fibrosis (CF) due to ventilatory limitations and fluctuating health status. Our aim was to determine if children with CF could regulate the intensity of cycle ergometer and treadmill exercise using target ratings of perceived exertion (RPE) derived from the Children's OMNI Scale. We examined prescription congruence (similar oxygen consumption [VO₂] and heart rate [HR] for target RPE) and intensity discrimination (different VO₂ and HR for different RPEs), from cycle to cycle and cycle to treadmill. Subjects were 24 children (12 male, 12 female), aged 10-17 years with varying disease severity. Each child participated in one orientation, one estimation trial (graded maximal exercise test), and two production trials (cycle and treadmill, alternating between RPE 4 and 7). At RPE 4, congruence was evident for both VO₂ and HR on the treadmill. On the cycle at RPE 4, VO₂ was significantly higher only in the first production trial, although HRs tended to be higher in the production trials than the estimation trial. Prescription congruence was also supported at RPE 7, with no significant differences in VO₂ or HR between estimation and production trials on cycle or treadmill. Results fully supported intensity discrimination, with significant differences between VO₂ and HR at RPE 4 and 7 (P < 0.0001). Children with CF appear capable of using the OMNI Scale to regulate cycle and treadmill exercise intensity. Training using this methodology has the potential to promote fitness in children with CF of varying severity.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulating intensity using perceived exertion during extended exercise periods.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2003 Jun;89(5):475-82. doi: 10.1007/s00421-003-0811-9. Epub 2003 Apr 24. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12712344 Clinical Trial.
-
Intensity selection and regulation using the OMNI scale of perceived exertion during intermittent exercise.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2013 Sep;38(9):960-6. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2012-0446. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2013. PMID: 23905662
-
A normalized rate of perceived exertion at ventilatory breakpoint for different exercise modalities and production of exercise intensity with self-regulation for Singapore children.J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2022 Dec;62(12):1630-1637. doi: 10.23736/S0022-4707.22.13411-0. Epub 2022 Mar 22. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2022. PMID: 35315991
-
The use of ratings of perceived exertion for exercise prescription in patients receiving beta-blocker therapy.Sports Med. 1996 Mar;21(3):176-90. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199621030-00003. Sports Med. 1996. PMID: 8776008 Review.
-
Perceived exertion : influence of age and cognitive development.Sports Med. 2006;36(11):911-28. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200636110-00001. Sports Med. 2006. PMID: 17052130 Review.
Cited by
-
Overall and differentiated sensory responses to cardiopulmonary exercise test in patients with cystic fibrosis: kinetics and ability to predict peak oxygen uptake.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2018 Sep;118(9):2007-2019. doi: 10.1007/s00421-018-3923-y. Epub 2018 Jul 9. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29987367
-
An Examination and Critique of Subjective Methods to Determine Exercise Intensity: The Talk Test, Feeling Scale, and Rating of Perceived Exertion.Sports Med. 2022 Sep;52(9):2085-2109. doi: 10.1007/s40279-022-01690-3. Epub 2022 May 4. Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 35507232 Review.
-
Physical exercise as a tool to minimize the consequences of the Covid-19 quarantine: An overview for cystic fibrosis.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020 Nov;55(11):2877-2882. doi: 10.1002/ppul.25041. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020. PMID: 32841519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parent and child perceptions of a self-regulated, home-based exercise program for children with cystic fibrosis.Nurs Res. 2013 Sep-Oct;62(5):305-14. doi: 10.1097/NNR.0b013e3182a03503. Nurs Res. 2013. PMID: 23995464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Orenstein DM, Noyes BE. Cystic fibrosis. In: Casaburi R, Petty TL, editors. Principles and practice of pulmonary rehabilitation. Philadephia: JB Saunders; 1993. p. 444.
-
- Orenstein DM, Rosenstein BJ, Stern RC. Cystic fibrosis: medical care. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams, & Wilkins; 2000. p. 3.
-
- Blau H, Mussaffo-Georgy H, Fink G, Kaye C, Szeinberg A, Spitzer S, Yahav J. Effects of an intensive 4-week summer camp on cystic fibrosis. Chest. 2002;121:1117–1122. - PubMed
-
- Gruber W, Orenstein DM, Braumann KM, Huls G. Health-related fitness and trainability in children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2008;43:953–64. - PubMed
-
- Orenstein DM, Franklin BA, Doershuk CF, Hellerstein HK, Germann KJ, Horowitz JG, Stern RC. Exercise conditioning and cardiopulmonary fitness in cystic fibrosis. The effects of a three-month supervised running program. Chest. 1981;80:392–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical