Deficiency of the calcium-sensing receptor in the kidney causes parathyroid hormone-independent hypocalciuria
- PMID: 22997254
- PMCID: PMC3482734
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2012030323
Deficiency of the calcium-sensing receptor in the kidney causes parathyroid hormone-independent hypocalciuria
Abstract
Rare loss-of-function mutations in the calcium-sensing receptor (Casr) gene lead to decreased urinary calcium excretion in the context of parathyroid hormone (PTH)-dependent hypercalcemia, but the role of Casr in the kidney is unknown. Using animals expressing Cre recombinase driven by the Six2 promoter, we generated mice that appeared grossly normal but had undetectable levels of Casr mRNA and protein in the kidney. Baseline serum calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, and PTH levels were similar to control mice. When challenged with dietary calcium supplementation, however, these mice had significantly lower urinary calcium excretion than controls (urinary calcium to creatinine, 0.31±0.03 versus 0.63±0.14; P=0.001). Western blot analysis on whole-kidney lysates suggested an approximately four-fold increase in activated Na(+)-K(+)-2Cl(-) cotransporter (NKCC2). In addition, experimental animals exhibited significant downregulation of Claudin14, a negative regulator of paracellular cation permeability in the thick ascending limb, and small but significant upregulation of Claudin16, a positive regulator of paracellular cation permeability. Taken together, these data suggest that renal Casr regulates calcium reabsorption in the thick ascending limb, independent of any change in PTH, by increasing the lumen-positive driving force for paracellular Ca(2+) transport.
Figures

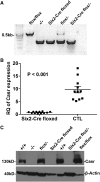


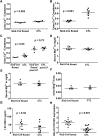
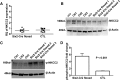
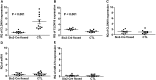
Comment in
-
Parathyroid hormone-independent role for the calcium-sensing receptor in the control of urinary calcium excretion.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Nov;23(11):1766-8. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2012090955. Epub 2012 Oct 18. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 23085632 No abstract available.
References
-
- Civitelli R, Ziambaras K: Calcium and phosphate homeostasis: Concerted interplay of new regulators. J Endocrinol Invest 34[Suppl]: 3–7, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Brown EM, Gamba G, Riccardi D, Lombardi M, Butters R, Kifor O, Sun A, Hediger MA, Lytton J, Hebert SC: Cloning and characterization of an extracellular Ca(2+)-sensing receptor from bovine parathyroid. Nature 366: 575–580, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Riccardi D, Kemp PJ: The calcium-sensing receptor beyond extracellular calcium homeostasis: Conception, development, adult physiology, and disease. Annu Rev Physiol 74: 271–297, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Brown EM, Pollak M, Riccardi D, Hebert SC: Cloning and characterization of an extracellular Ca(2+)-sensing receptor from parathyroid and kidney: New insights into the physiology and pathophysiology of calcium metabolism. Nephrol Dial Transplant 9: 1703–1706, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Brown EM, Pollak M, Hebert SC: The extracellular calcium-sensing receptor: Its role in health and disease. Annu Rev Med 49: 15–29, 1998 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

