Fractional anisotropy distributions in 2- to 6-year-old children with autism
- PMID: 22998325
- PMCID: PMC3606640
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.2012.01599.x
Fractional anisotropy distributions in 2- to 6-year-old children with autism
Abstract
Background: Increasing evidence suggests that autism is a disorder of distributed neural networks that may exhibit abnormal developmental trajectories. Characterisation of white matter early in the developmental course of the disorder is critical to understanding these aberrant trajectories.
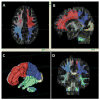
Methods: A cross-sectional study of 2- to 6-year-old children with autism was conducted using diffusion tensor imaging combined with a novel statistical approach employing fractional anisotropy distributions. Fifty-eight children aged 18-79 months were imaged: 33 were diagnosed with autism, 8 with general developmental delay, and 17 were typically developing. Fractional anisotropy values within global white matter, cortical lobes and the cerebellum were measured and transformed to random F distributions for each subject. Each distribution of values for a region was summarised by estimating δ, the estimated mean and standard deviation of the approximating F for each distribution.
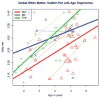
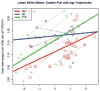
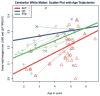
Results: The estimated δ parameter, , was significantly decreased in individuals with autism compared to the combined control group. This was true in all cortical lobes, as well as in the cerebellum, but differences were most robust in the temporal lobe. Predicted developmental trajectories of across the age range in the sample showed patterns that partially distinguished the groups. Exploratory analyses suggested that the variability, rather than the central tendency, component of was the driving force behind these results.
Conclusions: While preliminary, our results suggest white matter in young children with autism may be abnormally homogeneous, which may reflect poorly organised or differentiated pathways, particularly in the temporal lobe, which is important for social and emotional cognition.
Keywords: autism; brain; developmental; diffusion tensor imaging; fractional anisotropy; white matter.
© 2012 The Authors. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research © 2012 John Wiley & Sons Ltd, MENCAP & IASSID.
Figures
References
-
- Adolphs R, Sears L, Piven J. Abnormal processing of social information from faces in autism. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2001;11:231–9. - PubMed
-
- Alexander AL, Lee JE, Lazar M, Boudos R, DuBray MB, Oakes TR, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of the corpus callosum in autism. NeuroImage. 2007;34:61–73. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG, Corbett BA. The amygdala, autism, and anxiety. Novartis Foundation Symposium. 2003;251:177–87. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4. American Psychiatric Association; Arlington, VA: 2000. Text Revision.
-
- Aylward EH, Minshew NJ, Goldstein G, Honeycutt NA, Augustine AM, Yates KO, et al. MRI volumes of amygdala and hippocampus in non-mentally retarded autistic adolescents and adults. Neurology. 1999;53:2145–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

