Non-amyloid and amyloid prion protein deposits in prion-infected mice differ in blockage of interstitial brain fluid
- PMID: 22998478
- PMCID: PMC3567241
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.2012.01303.x
Non-amyloid and amyloid prion protein deposits in prion-infected mice differ in blockage of interstitial brain fluid
Abstract
Aims: Prion diseases are characterized by brain deposits of misfolded aggregated protease-resistant prion protein (PrP), termed PrPres. In humans and animals, PrPres is found as either disorganized non-amyloid aggregates or organized amyloid fibrils. Both PrPres forms are found in extracellular spaces of the brain. Thus, both might block drainage of brain interstitial fluid (ISF). The present experiments studied whether ISF blockage occurred during amyloid and/or non-amyloid prion diseases.
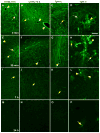
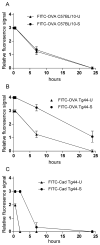
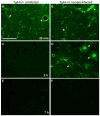
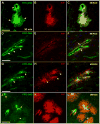
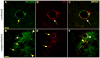
Methods: Various-sized fluorescein-labelled ISF tracers were stereotactically inoculated into the striatum of adult mice. At times from 5 min to 77 h, uninfected and scrapie-infected mice were compared. C57BL/10 mice expressing wild-type anchored PrP, which develop non-amyloid PrPres similar to humans with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, were compared with Tg44+/+ mice (transgenic mice secreting anchorless PrP) expressing anchorless PrP, which develop amyloid PrPres similar to certain human familial prion diseases.
Results: In C57BL/10 mice, extensive non-amyloid PrPres aggregate deposition was not associated with abnormal clearance kinetics of tracers. In contrast, scrapie-infected Tg44+/+ mice showed blockage of tracer clearance and colocalization of tracer with perivascular PrPres amyloid.
Conclusions: As tracer localization and clearance was normal in infected C57BL/10 mice, ISF blockage was not an important pathogenic mechanism in this model. Therefore, ISF blockage is unlikely to be a problem in non-amyloid human prion diseases such as sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. In contrast, partial ISF blockage appeared to be a possible pathogenic mechanism in Tg44+/+ mice. Thus this mechanism might also influence human amyloid prion diseases where expression of anchorless or mutated PrP results in perivascular amyloid PrPres deposition and cerebral amyloid angiopathy.
Published 2012. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures

References
-
- Parchi P, Giese A, Capellari S, Brown P, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Windl O, Zerr I, Budka H, Kopp N, Piccardo P, Poser S, Rojiani A, Streichemberger N, Julien J, Vital C, Ghetti B, Gambetti P, Kretzschmar H. Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease based on molecular and phenotypic analysis of 300 subjects. Ann Neurol. 1999;46:224–33. - PubMed
-
- Budka H, Aguzzi A, Brown P, Brucher JM, Bugiani O, Gullotta F, Haltia M, Hauw JJ, Ironside JW, Jellinger K, et al. Neuropathological diagnostic criteria for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) and other human spongiform encephalopathies (prion diseases) Brain Pathol. 1995;5:459–66. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez L, Martin S, Begara-McGorum I, Hunter N, Houston F, Simmons M, Jeffrey M. Effects of agent strain and host genotype on PrP accumulation in the brain of sheep naturally and experimentally affected with scrapie. J Comp Pathol. 2002;126:17–29. - PubMed
-
- Jeffrey M, Goodsir CM, Bruce ME, McBride PA, Fraser JR. In vivo toxicity of prion protein in murine scrapie: ultrastructural and immunogold studies. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1997;23:93–101. - PubMed
-
- Ghetti B, Piccardo P, Frangione B, Bugiani O, Giaccone G, Young K, Prelli F, Farlow MR, Dlouhy SR, Tagliavini F. Prion protein amyloidosis. Brain Pathol. 1996;6:127–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

