Antimicrobial susceptibility of porcine Brachyspira hyodysenteriae and Brachyspira pilosicoli isolated in Sweden between 1990 and 2010
- PMID: 22998753
- PMCID: PMC3526423
- DOI: 10.1186/1751-0147-54-54
Antimicrobial susceptibility of porcine Brachyspira hyodysenteriae and Brachyspira pilosicoli isolated in Sweden between 1990 and 2010
Abstract
Background: The anaerobic spirochetes Brachyspira hyodysenteriae and Brachyspira pilosicoli cause diarrheal diseases in pigs. Their fastidious nature has hampered standardization of methods for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. For monitoring of antimicrobial susceptibility wild type cutoff values are needed to define where the wild type distribution of MICs ends and no approved cutoffs are available for Brachyspira spp. In this study antimicrobial susceptibility data for both species (in total 906 isolates) were compiled and analyzed and wild type cut off values for B. hyodysenteriae proposed.
Methods: The MICs of tiamulin, valnemulin, tylosin, tylvalosin, doxycycline and lincomycin were determined by broth dilution in brain heart infusion broth supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum.
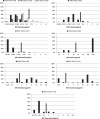
Results: The compiled MICs from the broth dilution tests of the B. hyodysenteriae type strain, B78T (ATCC® 27164T), showed that the method yields reproducible results. In an international perspective the frequencies of isolates with decreased antimicrobial susceptibility were low among both B. hyodysenteriae and B. pilosicoli. However, in B. pilosicoli a constant level of 10-15% isolates with tiamulin MICs >4 μg/ml was detected between 2002 and 2010 and in B. hyodysenteriae a gradual increase in tiamulin MICs was seen between 1990 and 2003 although this increase has ceased during the last years. The wild type cutoff values proposed for B. hyodysenteriae are: tiamulin >0.25 μg/ml, valnemulin >0.125 μg/ml, tylosin >16 μg/ml, tylvalosin >1 μg/ml, lincomycin >1 μg/ml and doxycycline >0.5 μg/ml.
Conclusions: The broth dilution method used in this study has over the years generated tightly grouped MIC populations for the field isolates and reproducible results for the control strain B78T and is therefore a suitable antimicrobial susceptibility test method for monitoring of Brachyspira spp. Here we propose wild type cutoff values for six antimicrobial agents for B. hyodysenteriae tested by broth dilution based on MIC distributions and the current knowledge on mechanisms of resistance in this species. There are few studies on antimicrobial resistance mechanisms and MIC distributions in B. pilosicoli but to some extent the cutoff values proposed for B. hyodysenteriae may be applicable also for monitoring of antimicrobial susceptibility in B. pilosicoli.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Susceptibility to pleuromutilins in Brachyspira (Serpulina) hyodysenteriae.Anim Health Res Rev. 2001 Jun;2(1):59-65. Anim Health Res Rev. 2001. PMID: 11708748
-
Comparison of agar dilution and antibiotic gradient strip test with broth microdilution for susceptibility testing of swine Brachyspira species.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2016 Mar;28(2):133-43. doi: 10.1177/1040638716629154. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2016. PMID: 26965233
-
Antimicrobial susceptibility of Brachyspira hyodysenteriae in Switzerland.Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 2016 Jun;158(6):405-10. doi: 10.17236/sat00066. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 2016. PMID: 27504836 English.
-
Pleuromutilins: use in food-producing animals in the European Union, development of resistance and impact on human and animal health.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014 Aug;69(8):2022-31. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku123. Epub 2014 May 3. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24793902 Review.
-
A review of methods used for studying the molecular epidemiology of Brachyspira hyodysenteriae.Vet Microbiol. 2017 Aug;207:181-194. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.06.011. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Vet Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28757022 Review.
Cited by
-
First identification of "Brachyspira hampsonii" in wild European waterfowl.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 4;8(12):e82626. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082626. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24349322 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Genome Sequencing of Brachyspira hyodysenteriae Isolates From England and Wales Reveals Similarities to European Isolates and Mutations Associated With Reduced Sensitivity to Antimicrobials.Front Microbiol. 2021 Aug 31;12:713233. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.713233. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34531838 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation and evaluation of different eradication strategies for Brachyspira hyodysenteriae.Porcine Health Manag. 2020 Sep 14;6:27. doi: 10.1186/s40813-020-00162-2. eCollection 2020. Porcine Health Manag. 2020. PMID: 32944272 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Resistance in Clostridium and Brachyspira spp. and Other Anaerobes.Microbiol Spectr. 2020 Jan;8(1):10.1128/microbiolspec.arba-0020-2017. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.ARBA-0020-2017. Microbiol Spectr. 2020. PMID: 31971162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro susceptibility of Brachyspira hyodysenteriae to organic acids and essential oil components.J Vet Med Sci. 2016 Feb;78(2):325-8. doi: 10.1292/jvms.15-0341. Epub 2015 Sep 14. J Vet Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 26369432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taylor DJ, Alexander TJ. The production of dysentery in swine by feeding cultures containing a spirochaete. Br Vet J. 1971;127:58–61. - PubMed
-
- Hidalgo A, Carvajal A, Vester B, Pringle M, Naharro G, Rubio P. Trends towards lower antimicrobial susceptibility and characterization of acquired resistance among clinical isolates of Brachyspira hyodysenteriae in Spain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55:3330–3337. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01749-10. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

