Nutraceutical pill containing berberine versus ezetimibe on plasma lipid pattern in hypercholesterolemic subjects and its additive effect in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia on stable cholesterol-lowering treatment
- PMID: 22998978
- PMCID: PMC3477057
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-11-123
Nutraceutical pill containing berberine versus ezetimibe on plasma lipid pattern in hypercholesterolemic subjects and its additive effect in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia on stable cholesterol-lowering treatment
Abstract
Background: Although statins (STs) are drugs of first choice in hypercholesterolemic patients, especially in those at high cardiovascular risk, some of them are intolerant to STs or refuse treatment with these drugs. In view of this, we have evaluated the lipid-lowering effect of a nutraceutical pill containing berberine (BBR) and of ezetimibe, as alternative treatments, in monotherapy or in combination, in 228 subjects with primary hypercholesterolemia (HCH), with history of STs intolerance or refusing STs treatment. In addition, since PCSK9 was found up-regulated by STs dampening their effect through an LDL receptors (LDLRs) degradation, and BBR suppressed PCSK9 expression in cellular studies, we supplemented the stable lipid-lowering therapy of 30 genotype-confirmed Familial Hypercholesterolemia heterozygotes (HeFH) with BBR, searching for a further plasma cholesterol reduction. Plasma lipid pattern was evaluated at baseline and during treatments.
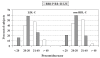
Results: In HCH subjects the nutraceutical pill resulted more effective than EZE in lowering LDL cholesterol (-31.7% vs -25.4%, P < 0.001) and better tolerated. On treatment, LDL-C level below 3.36 mmol/L (≤130 mg/dl) was observed in 28.9% of subjects treated with the nutraceutical pill and 11.8% of those treated with EZE (P <0.007). In the group treated with EZE the subjects carrying the G allele of the g.1679 C > G silent polymorphism of NPC1L1 gene showed a higher response to EZE than homozygous for the common allele (GG + CG: LDL-C -29.4±5.0%, CC -23.6±6.5%, P <0.001). Combined treatment with these drugs was as effective as STs in moderate doses (LDL cholesterol -37%, triglycerides -23%). In HeFH patients the addition of BBR resulted in LDL cholesterol reductions inversely related to those induced by the stable therapy (r = -0.617, P <0.0001), with mean 10.5% further decrease.
Conclusions: The alternative treatments tested in our HCH subjects were rather effective and safe. The findings in HeFH patients suggest that BBR might act in vivo increasing expression and stability of LDLRs and/or suppressing PCSK9 expression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, factorial design study to evaluate the lipid-altering efficacy and safety profile of the ezetimibe/simvastatin tablet compared with ezetimibe and simvastatin monotherapy in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia.Clin Ther. 2004 Nov;26(11):1758-73. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2004.11.016. Clin Ther. 2004. PMID: 15639688 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of ezetimibe on plasma lipoproteins in severely hypercholesterolemic patients treated with regular LDL-apheresis and statins.Atherosclerosis. 2005 May;180(1):107-12. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2004.11.007. Epub 2004 Dec 29. Atherosclerosis. 2005. PMID: 15823282 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of ezetimibe added to on-going statin therapy on the lipid profile of hypercholesterolemic patients with diabetes mellitus or metabolic syndrome.Curr Med Res Opin. 2004 Sep;20(9):1437-45. doi: 10.1185/030079904x2321. Curr Med Res Opin. 2004. PMID: 15383192 Clinical Trial.
-
[Ezetimibe: from pharmacology to clinical trials].Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2003 Dec;64(6):442-7. Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2003. PMID: 15067249 Review. French.
-
Berberine, a plant alkaloid with lipid- and glucose-lowering properties: From in vitro evidence to clinical studies.Atherosclerosis. 2015 Dec;243(2):449-61. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.09.032. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Atherosclerosis. 2015. PMID: 26520899 Review.
Cited by
-
Nutraceuticals in the management of patients with statin-associated muscle symptoms, with a note on real-world experience.Clin Cardiol. 2018 Jan;41(1):159-165. doi: 10.1002/clc.22862. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Clin Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29363784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of poly-bioactive compounds on lipid profile and body weight in a moderately hypercholesterolemic population with low cardiovascular disease risk: a multicenter randomized trial.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 1;9(8):e101978. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101978. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25084280 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phytopharmacology and Clinical Updates of Berberis Species Against Diabetes and Other Metabolic Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Feb 18;11:41. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00041. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32132921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Armolipid Plus on small dense LDL particles in a sample of patients affected by familial combined hyperlipidemia.Clin Lipidol. 2015 Dec;10(6):475-480. doi: 10.2217/clp.15.37. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Clin Lipidol. 2015. PMID: 27066111 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of a New Generation of Nutraceutical Compounds on Lipid Profile and Glycaemia in Subjects with Pre-hypertension.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2019 Aug;26(4):345-350. doi: 10.1007/s40292-019-00332-6. Epub 2019 Jul 27. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2019. PMID: 31352663 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Catapano AL, Reiner Z, De Backer G, Grahan I, Taskinen M-R, Wiklund O, Agewall S, Alegria E, Chapman MJ, Durrington P, Erdine S, Halcox J, Hobbs R, Kjekshus J, Perrone Filardi P, Riccardi G, Storey R, Wood D. ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias. The Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) Atherosclerosis. 2011;217S:S1–S44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

