Insulin resistance and heart failure: molecular mechanisms
- PMID: 22999243
- PMCID: PMC3457065
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hfc.2012.06.005
Insulin resistance and heart failure: molecular mechanisms
Abstract
This article addresses the issue of insulin resistance and associated reductions in cardiac insulin metabolic signaling, which is emerging as a major factor in the development of heart failure, and assumes more importance because of an epidemic increase in obesity and the cardiorenal metabolic syndrome in our aging population. The effects of cardiac insulin resistance are exacerbated by metabolic, endocrine, and cytokine alterations associated with systemic insulin resistance. Understanding the molecular mechanisms linking insulin resistance and heart failure may help to design new and more effective mechanism-based drugs to improve myocardial and systemic insulin resistance.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
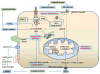
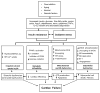
References
-
- Norton C, Georgiopoulou VV, Kalogeropoulos AP, et al. Epidemiology and cost of advanced heart failure. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2011;54:78–85. - PubMed
-
- Falcão-Pires I, Leite-Moreira AF. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: understanding the molecular and cellular basis to progress in diagnosis and treatment. Heart Fail Rev. 2011 May 28; - PubMed
-
- Reaven GM. Insulin resistance: the link between obesity and cardiovascular disease. Med Clin North Am. 2011;95:875–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

