Crystal structures of 70S ribosomes bound to release factors RF1, RF2 and RF3
- PMID: 22999888
- PMCID: PMC3982307
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2012.08.004
Crystal structures of 70S ribosomes bound to release factors RF1, RF2 and RF3
Abstract
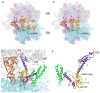
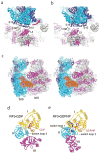
Termination is a crucial step in translation, most notably because premature termination can lead to toxic truncated polypeptides. Most interesting is the fact that stop codons are read by a completely different mechanism from that of sense codons. In recent years, rapid progress has been made in the structural biology of complexes of bacterial ribosomes bound to translation termination factors, much of which has been discussed in earlier reviews [1-5]. Here, we present a brief overview of the structures of bacterial translation termination complexes. The first part summarizes what has been learned from crystal structures of complexes containing the class I release factors RF1 and RF2. In the second part, we discuss the results and implications of two recent X-ray structures of complexes of ribosomes bound to the translational GTPase RF3. These structures have provided many insights and a number of surprises. While structures alone do not tell us how these complicated molecular assemblies work, is it nevertheless clear that it will not be possible to understand their mechanisms without detailed structural information.
Copyright © 2012. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures


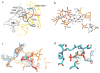

References
-
- Klaholz BP. Molecular recognition and catalysis in translation termination complexes. Trends Biochem Sci. 2011;36:282–292. - PubMed
-
- Loh PG, Song H. Structural and mechanistic insights into translation termination. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2010;20:98–103. - PubMed
-
- Dunkle JA, Cate JH. Ribosome structure and dynamics during translocation and termination. Annu Rev Biophys. 2011;39:227–244. - PubMed
-
- Petry S, Weixlbaumer A, Ramakrishnan V. The termination of translation. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008;18:70–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

